(continued)
A little fern, A LOT of genes ...
The Horsemen ...
Oh my, the things we spread ... good and not ...
AI vs Plastic ...
Si, si AI ...
Part man, part Tardigrade ...
That's using your brains! ...
It seems that they break this record every few weeks now ...
A topic dear to my heart ... to make it more likely that we will see the future of the universe ...
Gassho, J
stlah
A little fern, A LOT of genes ...
Unlocking the Genetic Giant: Tiny Fern Has the Largest Genome of Any Organism on Earth
Researchers have identified Tmesipteris oblanceolata, a fern from New Caledonia, as having the largest genome recorded, surpassing the previous record-holder Paris japonica. This discovery, detailed in the iScience journal, reveals that this fern contains over 50 times more DNA than humans and highlights the significant implications larger genomes have on plant biology and adaptation. ...
Researchers have identified Tmesipteris oblanceolata, a fern from New Caledonia, as having the largest genome recorded, surpassing the previous record-holder Paris japonica. This discovery, detailed in the iScience journal, reveals that this fern contains over 50 times more DNA than humans and highlights the significant implications larger genomes have on plant biology and adaptation. ...
- Stretched out, the Tmesipteris oblanceolata genome is taller than Big Ben’s tower in London
- Discovery poses new questions about just how much DNA can be stored in cells
BEWARE THE THREE HORSEMEN OF THE OCEAN APOCALYPSE.
Extreme heat, acidification, and deoxygenation are all fearsome forces on their own. Combine two or more of them, and they can be catastrophic: they cause what's known as column-compound extreme events (CCX), which turn affected areas of the ocean virtually uninhabitable.
The research, which focused on the effects in the upper one thousand feet of the ocean, found that these compound events are growing, and now threaten up to 20 percent of global ocean volume. The waters of the North Pacific and the tropics are the most hard hit, as the only areas faced with full-blown triple CCX — at least so far.
To make matters worse, the events are only getting more extreme, lasting three times longer — up to 30 days — and are six times more intense compared to the 1960s, per the Guardian. And wherever they occur, they can cut down the amount of habitable space by up to 75 percent.
"The impacts of this have already been seen and felt," study lead author Joel Wong, a researcher at ETH Zurich, told the newspaper. "Intense extreme events like these are likely to happen again in the future and will disrupt marine ecosystems and fisheries around the world."
LINK
Extreme heat, acidification, and deoxygenation are all fearsome forces on their own. Combine two or more of them, and they can be catastrophic: they cause what's known as column-compound extreme events (CCX), which turn affected areas of the ocean virtually uninhabitable.
The research, which focused on the effects in the upper one thousand feet of the ocean, found that these compound events are growing, and now threaten up to 20 percent of global ocean volume. The waters of the North Pacific and the tropics are the most hard hit, as the only areas faced with full-blown triple CCX — at least so far.
To make matters worse, the events are only getting more extreme, lasting three times longer — up to 30 days — and are six times more intense compared to the 1960s, per the Guardian. And wherever they occur, they can cut down the amount of habitable space by up to 75 percent.
"The impacts of this have already been seen and felt," study lead author Joel Wong, a researcher at ETH Zurich, told the newspaper. "Intense extreme events like these are likely to happen again in the future and will disrupt marine ecosystems and fisheries around the world."
LINK
REMOTE AMAZON TRIBE FINALLY GETS INTERNET, GETS HOOKED ON PORN AND SOCIAL MEDIA
The New York Times reports on what may sound a bit familiar: young people poring over social media feeds, streaming soccer games, and of course, gossiping over WhatsApp. Evenings are spent lounging around on their phones and playing first-person shooters and other video games.
"When it arrived, everyone was happy," said Tsainama Marubo, 73. "But now, things have gotten worse."
Some of the young men are especially getting a kick out of it. Alfredo Marubo, a leader of an association of the tribe's villages, lamented that the boys, now with their own group chats, were sharing porn and other explicit videos — which is unprecedented in their culture that considers kissing in public taboo.... "Everyone is so connected that sometimes they don't even talk to their own family," he told the NYT.
Tsainama echoed those fears, but was more conflicted. "Young people have gotten lazy because of the internet," she said. "They're learning the ways of the white people. But please don't take our internet away." ... New job opportunities have opened up. Villages can now easily coordinate over group chats, and also reach out to local authorities.
"It's already saved lives," Enoque Marubo, who was one of the first in the tribe to push for an internet connection, told the NYT, such as in the case of venomous snakebites, which need immediate medical treatment.
"The leaders have been clear," he added. "We can't live without the internet."
LINK
The New York Times reports on what may sound a bit familiar: young people poring over social media feeds, streaming soccer games, and of course, gossiping over WhatsApp. Evenings are spent lounging around on their phones and playing first-person shooters and other video games.
"When it arrived, everyone was happy," said Tsainama Marubo, 73. "But now, things have gotten worse."
Some of the young men are especially getting a kick out of it. Alfredo Marubo, a leader of an association of the tribe's villages, lamented that the boys, now with their own group chats, were sharing porn and other explicit videos — which is unprecedented in their culture that considers kissing in public taboo.... "Everyone is so connected that sometimes they don't even talk to their own family," he told the NYT.
Tsainama echoed those fears, but was more conflicted. "Young people have gotten lazy because of the internet," she said. "They're learning the ways of the white people. But please don't take our internet away." ... New job opportunities have opened up. Villages can now easily coordinate over group chats, and also reach out to local authorities.
"It's already saved lives," Enoque Marubo, who was one of the first in the tribe to push for an internet connection, told the NYT, such as in the case of venomous snakebites, which need immediate medical treatment.
"The leaders have been clear," he added. "We can't live without the internet."
LINK
Scientists used machine learning to discover what they say could be a new way to speed up the process of breaking down plastic significantly
As detailed in a new paper published in the journal Nature, a research team from the University of Texas at Austin modified an enzyme to break down the individual components of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a commonly used plastic that makes up a staggering 12 percent of global waste.
Impressively, the modified enzyme also reduced the amount of time it takes for the plastic to degrade from months to a just single week.
The process, called depolymerization, has the added benefit of allowing the broken down monomers to be reconstituted back into virgin PET plastic, a potentially revolutionary way of recycling the astronomical amounts of plastic waste we've accumulated.
That all depends, though, on figuring out a reliable and affordable way to scale up and industrialize the process.
LIKE
As detailed in a new paper published in the journal Nature, a research team from the University of Texas at Austin modified an enzyme to break down the individual components of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a commonly used plastic that makes up a staggering 12 percent of global waste.
Impressively, the modified enzyme also reduced the amount of time it takes for the plastic to degrade from months to a just single week.
The process, called depolymerization, has the added benefit of allowing the broken down monomers to be reconstituted back into virgin PET plastic, a potentially revolutionary way of recycling the astronomical amounts of plastic waste we've accumulated.
That all depends, though, on figuring out a reliable and affordable way to scale up and industrialize the process.
LIKE
Bilingual AI brain implant helps stroke survivor communicate in Spanish and English
The implant uses a form of AI to turn the man's brain activity into sentences, allowing him to participate in a bilingual conversation and "switch between languages."
... Nearly a dozen scientists from the university’s Center for Neural Engineering and Prostheses have worked for several years to design a decoding system that could turn the man's brain activity into sentences in both languages and display them on a screen.
An article published May 20 in Nature Biomedical Engineering outlining their research identifies the man as Pancho. At age 20, he became severely paralyzed as a result of a stroke he had in the early 2000s. Pancho can moan and grunt but can't articulate clear words. He is a native Spanish speaker who learned English as an adult.
...
LINK
The implant uses a form of AI to turn the man's brain activity into sentences, allowing him to participate in a bilingual conversation and "switch between languages."
... Nearly a dozen scientists from the university’s Center for Neural Engineering and Prostheses have worked for several years to design a decoding system that could turn the man's brain activity into sentences in both languages and display them on a screen.
An article published May 20 in Nature Biomedical Engineering outlining their research identifies the man as Pancho. At age 20, he became severely paralyzed as a result of a stroke he had in the early 2000s. Pancho can moan and grunt but can't articulate clear words. He is a native Spanish speaker who learned English as an adult.
...
LINK
SCIENTISTS SPLICE MATERIAL FROM CREATURE THAT CAN SURVIVE OUTER SPACE INTO HUMAN CELLS
In a new study led by the University of Wyoming, an international team of researchers found that when looking into the incredible durability of the itty bitty tardigrade — known affectionately as the "water bear" or "moss piglet" — proteins from the creature might help slow aging in humans, too. ... "Amazingly, when we introduce these proteins into human cells, they gel and slow down metabolism, just like in tardigrades," Silvia Sanchez-Martinez, a senior research scientist at UW's molecular biology department and the lead author of the study, said in the school's statement. "Just like tardigrades, when you put human cells that have these proteins into biostasis, they become more resistant to stresses, conferring some of the tardigrades' abilities to the human cells." ...
LINK
In a new study led by the University of Wyoming, an international team of researchers found that when looking into the incredible durability of the itty bitty tardigrade — known affectionately as the "water bear" or "moss piglet" — proteins from the creature might help slow aging in humans, too. ... "Amazingly, when we introduce these proteins into human cells, they gel and slow down metabolism, just like in tardigrades," Silvia Sanchez-Martinez, a senior research scientist at UW's molecular biology department and the lead author of the study, said in the school's statement. "Just like tardigrades, when you put human cells that have these proteins into biostasis, they become more resistant to stresses, conferring some of the tardigrades' abilities to the human cells." ...
LINK
SCIENTISTS CONNECT 16 MINI BRAINS MADE OF HUMAN TISSUE TO CREATE A "LIVING COMPUTER"
Switzerland-based startup FinalSpark claims to have built a unique computer processor made from 16 mini brains made from human brain tissue, Tom's Hardware reports — and they are positioning this "living computer" as an alternative to silicon-based computing.
And now, other researchers can remotely access the startup's biocomputer, the Neuroplatform, to conduct studies on, say, artificial intelligence, which typically requires enormous resources.
"One of the biggest advantages of biological computing is that neurons compute information with much less energy than digital computers," FinalSpark scientist and strategic advisor Ewelina Kurtys wrote in a company blog post earlier this month. "It is estimated that living neurons can use over 1 million times less energy than the current digital processors we use."
The startup takes brain organoids, small samples of human brain tissue derived from neural stem cells, and places them in a special environment that keeps these organoids alive. They then hook up these mini brains to specialized electrodes to perform computer processing and digital analog conversions to transform neural activity into digital information.
The concept of living computers has been around for quite some time now. Last year, for instance, scientists hooked up neurons to electrical circuits, resulting in a device that could perform voice recognition.
These unusual machines have some noteworthy advantages over their silicon-based counterparts, including a significantly smaller carbon footprint.
LINK
Switzerland-based startup FinalSpark claims to have built a unique computer processor made from 16 mini brains made from human brain tissue, Tom's Hardware reports — and they are positioning this "living computer" as an alternative to silicon-based computing.
And now, other researchers can remotely access the startup's biocomputer, the Neuroplatform, to conduct studies on, say, artificial intelligence, which typically requires enormous resources.
"One of the biggest advantages of biological computing is that neurons compute information with much less energy than digital computers," FinalSpark scientist and strategic advisor Ewelina Kurtys wrote in a company blog post earlier this month. "It is estimated that living neurons can use over 1 million times less energy than the current digital processors we use."
The startup takes brain organoids, small samples of human brain tissue derived from neural stem cells, and places them in a special environment that keeps these organoids alive. They then hook up these mini brains to specialized electrodes to perform computer processing and digital analog conversions to transform neural activity into digital information.
The concept of living computers has been around for quite some time now. Last year, for instance, scientists hooked up neurons to electrical circuits, resulting in a device that could perform voice recognition.
These unusual machines have some noteworthy advantages over their silicon-based counterparts, including a significantly smaller carbon footprint.
LINK
Webb Uncovers Most Distant Known Galaxy – “Most Significant Extragalactic Discovery to Date”
This infrared image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (also called Webb or JWST) was taken by the NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) for the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey, or JADES, program. The NIRCam data was used to determine which galaxies to study further with spectroscopic observations. One such galaxy, JADES-GS-z14-0 (shown in the pullout), was determined to be at a redshift of 14.32 (+0.08/-0.20), making it the current record-holder for the most distant known galaxy. This corresponds to a time less than 300 million years after the Big Bang.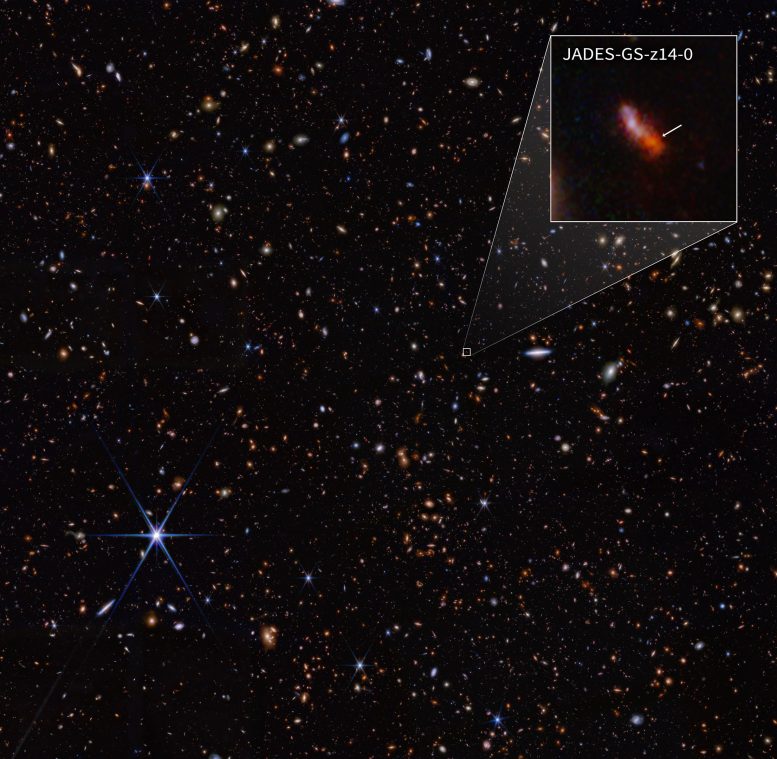
LINK
This infrared image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (also called Webb or JWST) was taken by the NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) for the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey, or JADES, program. The NIRCam data was used to determine which galaxies to study further with spectroscopic observations. One such galaxy, JADES-GS-z14-0 (shown in the pullout), was determined to be at a redshift of 14.32 (+0.08/-0.20), making it the current record-holder for the most distant known galaxy. This corresponds to a time less than 300 million years after the Big Bang.

LINK
How Brain Damage Illuminates the Pathways of Generosity
A study reveals that the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) plays a crucial role in our willingness to help others, impacting global challenges and treatments for social disorders. The research showed that damage to this brain region significantly reduces motivation to engage in prosocial behaviors. ... Patients with vmPFC damage were less willing to choose to help others, exerted less force on even after they did decide to help, and earned less money to help others compared to the control groups. ...
LINK
A study reveals that the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) plays a crucial role in our willingness to help others, impacting global challenges and treatments for social disorders. The research showed that damage to this brain region significantly reduces motivation to engage in prosocial behaviors. ... Patients with vmPFC damage were less willing to choose to help others, exerted less force on even after they did decide to help, and earned less money to help others compared to the control groups. ...
LINK
stlah

















 Oh my.
Oh my.


Comment