Did you feel it? 

Do you know that SATURN'S RINGS WILL DISAPPEAR SOON!!!! (well, for awhile) ...
(well, for awhile) ...
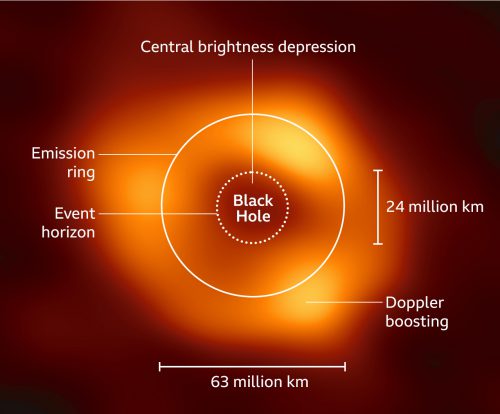
Shining a light on the dark ...
You can fly to Jupiter! ... or, at least, your name can ...
I posted this before, but worth mentioning again ...
This is not good news ...  ... although maybe will help with over-population
... although maybe will help with over-population 
And in case we stop reproducing ... this is faster than humans anyway ...
A chip off the old block ...
Ever see a pattern when sitting Zazen, facing the wall ...
... While Americans slowly return to being cavemen ...
Gassho, J
stlah

Cosmic Flash: Earth Struck by Historic Gamma-Ray Burst From Exploding Star
An enormous burst of gamma rays, detected by ESA’s Integral space telescope, has struck Earth [At 14:21 BST / 15:21 CEST on October 9, 2022]. The blast caused a significant disturbance in our planet’s ionosphere. Such disturbances are usually associated with energetic particle events on the Sun but this one was the result of an exploding star almost two billion light-years away. Analyzing the effects of the blast could provide information about the mass extinctions in Earth’s history.
... “It was probably the brightest gamma-ray burst we have ever detected,” says Mirko Piersanti, University of L’Aquila, Italy, and lead author of the team that published these results. ... So strong in fact that its nearest rival on record is ten times weaker. Statistically, a GRB as strong as GRB 221009A arrives at Earth only once every 10,000 years. ... Gamma-ray bursts were once mysterious events but are now recognized to be the outpouring of energy from exploding stars called supernovae, or from the collision of two super-dense neutron stars. ...
... This particular GRB took place in a galaxy almost 2 billion light-years away – hence two billion years ago – yet it still had enough energy to affect Earth. ...
https://scitechdaily.com/cosmic-flas...xploding-star/
An enormous burst of gamma rays, detected by ESA’s Integral space telescope, has struck Earth [At 14:21 BST / 15:21 CEST on October 9, 2022]. The blast caused a significant disturbance in our planet’s ionosphere. Such disturbances are usually associated with energetic particle events on the Sun but this one was the result of an exploding star almost two billion light-years away. Analyzing the effects of the blast could provide information about the mass extinctions in Earth’s history.
... “It was probably the brightest gamma-ray burst we have ever detected,” says Mirko Piersanti, University of L’Aquila, Italy, and lead author of the team that published these results. ... So strong in fact that its nearest rival on record is ten times weaker. Statistically, a GRB as strong as GRB 221009A arrives at Earth only once every 10,000 years. ... Gamma-ray bursts were once mysterious events but are now recognized to be the outpouring of energy from exploding stars called supernovae, or from the collision of two super-dense neutron stars. ...
... This particular GRB took place in a galaxy almost 2 billion light-years away – hence two billion years ago – yet it still had enough energy to affect Earth. ...
https://scitechdaily.com/cosmic-flas...xploding-star/

Do you know that SATURN'S RINGS WILL DISAPPEAR SOON!!!!
 (well, for awhile) ...
(well, for awhile) ...
Unveiling Saturn’s Secrets: Eclipses Reveal Ring Transparency
Τhe main rings, which extend up to 140,000 km (90,000 miles) from the planet, but have a maximum thickness of only 1 km (0.6 miles), are to disappear from view from Earth by 2025. In that year the rings will be tilted edge-on to Earth, making it almost impossible to view them. They will tilt back towards Earth during the next phase of Saturn’s 29-year orbit and will continue to become more visible and brighter until 2032.
...
https://scitechdaily.com/unveiling-s...-transparency/
Τhe main rings, which extend up to 140,000 km (90,000 miles) from the planet, but have a maximum thickness of only 1 km (0.6 miles), are to disappear from view from Earth by 2025. In that year the rings will be tilted edge-on to Earth, making it almost impossible to view them. They will tilt back towards Earth during the next phase of Saturn’s 29-year orbit and will continue to become more visible and brighter until 2032.
...
https://scitechdaily.com/unveiling-s...-transparency/
Cosmic Clarity: Gravitational Lensing Reveals the Fine Fabric of Dark Matter
A team of researchers has used the gravitational lensing of the MG J0414+0534 system, observed with ALMA, to map dark matter distribution in unprecedented detail, confirming theories of cold dark matter and paving the way for further discoveries about the universe’s dominant but elusive component. ... Mysterious dark matter accounts for most of the matter in the Universe. Dark matter is invisible and makes itself know only through its gravitational effects. Dark matter has never been isolated in a laboratory, so researchers must rely on “natural experiments” to study it.
[Below] Dark matter fluctuations in the lens system MG J0414+0534. The whitish blue color represents the gravitationally lensed images observed by ALMA. The calculated distribution of dark matter is shown in orange; brighter regions indicate higher concentrations of dark matter and dark orange regions indicate lower concentrations.

A team of researchers has used the gravitational lensing of the MG J0414+0534 system, observed with ALMA, to map dark matter distribution in unprecedented detail, confirming theories of cold dark matter and paving the way for further discoveries about the universe’s dominant but elusive component. ... Mysterious dark matter accounts for most of the matter in the Universe. Dark matter is invisible and makes itself know only through its gravitational effects. Dark matter has never been isolated in a laboratory, so researchers must rely on “natural experiments” to study it.
[Below] Dark matter fluctuations in the lens system MG J0414+0534. The whitish blue color represents the gravitationally lensed images observed by ALMA. The calculated distribution of dark matter is shown in orange; brighter regions indicate higher concentrations of dark matter and dark orange regions indicate lower concentrations.

Fly Your Name to Jupiter’s Moon: Join NASA’s Europa Odyssey
Six weeks remain for you to add your name to a microchip that will ride aboard the spacecraft as it explores Jupiter’s moon Europa.
[The process by which they do it is even more interesting!] ....
https://scitechdaily.com/fly-your-na...uropa-odyssey/
Six weeks remain for you to add your name to a microchip that will ride aboard the spacecraft as it explores Jupiter’s moon Europa.
[The process by which they do it is even more interesting!] ....
https://scitechdaily.com/fly-your-na...uropa-odyssey/
CRISPR treatment has been greenlit in UK in global first. Here’s who it could help
The United Kingdom has become the first country to give regulatory approval to a medical treatment involving the revolutionary CRISPR gene editing tool.
The country’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency said Thursday it had given a greenlight to a treatment known as Casgevy, which will be used to treat sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia. Both genetic conditions are caused by errors in the genes for hemoglobin, which is used by red blood cells to carry oxygen around the body. There is no known universally successful treatment for either disorder.
Sickle cell disease, which can result in attacks of debilitating pain, is more common in people with an African or Caribbean family background. Beta thalassemia mainly affects people of Mediterranean, South Asian, Southeast Asian and Middle Eastern origin, the statement said.
... The CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technique allows scientists to make very precise changes to DNA. Its inventors — Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer A. Doudna — won a Nobel Prize in chemistry in 2020.
Casgevy isn’t a simple pill or injection. The treatment, made by Vertex Pharmaceuticals, is administered by taking stem cells out of a patient’s bone marrow and editing a gene in the cells in a lab. Patients then must undergo a “conditioning treatment,” which can involve an immunosuppressing drug, radiotherapy or chemotherapy, to prepare the bone marrow before the modified cells are infused back into the patient, according to the MHRA.
“After that, patients may need to spend at least a month in a hospital facility while the treated cells take up residence in the bone marrow and start to make red blood cells with the stable form of haemoglobin,” according to the statement.
The US Food and Drug Administration is evaluating the same treatment and is expected to make a decision on whether to greenlight it by December 8. ... The release from the MHRA did not say how much the treatment would cost, but it’s likely to be expensive.
The United Kingdom has become the first country to give regulatory approval to a medical treatment involving the revolutionary CRISPR gene editing tool.
The country’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency said Thursday it had given a greenlight to a treatment known as Casgevy, which will be used to treat sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia. Both genetic conditions are caused by errors in the genes for hemoglobin, which is used by red blood cells to carry oxygen around the body. There is no known universally successful treatment for either disorder.
Sickle cell disease, which can result in attacks of debilitating pain, is more common in people with an African or Caribbean family background. Beta thalassemia mainly affects people of Mediterranean, South Asian, Southeast Asian and Middle Eastern origin, the statement said.
... The CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technique allows scientists to make very precise changes to DNA. Its inventors — Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer A. Doudna — won a Nobel Prize in chemistry in 2020.
Casgevy isn’t a simple pill or injection. The treatment, made by Vertex Pharmaceuticals, is administered by taking stem cells out of a patient’s bone marrow and editing a gene in the cells in a lab. Patients then must undergo a “conditioning treatment,” which can involve an immunosuppressing drug, radiotherapy or chemotherapy, to prepare the bone marrow before the modified cells are infused back into the patient, according to the MHRA.
“After that, patients may need to spend at least a month in a hospital facility while the treated cells take up residence in the bone marrow and start to make red blood cells with the stable form of haemoglobin,” according to the statement.
The US Food and Drug Administration is evaluating the same treatment and is expected to make a decision on whether to greenlight it by December 8. ... The release from the MHRA did not say how much the treatment would cost, but it’s likely to be expensive.
 ... although maybe will help with over-population
... although maybe will help with over-population 
Common pesticides in food reducing sperm count worldwide, study says
Pesticides used in our homes, gardens and lawns and sprayed on foods we eat are contributing to a dramatic decline in sperm count among men worldwide, according to a new analysis of studies over the last 50 years.
“Over the course of 50 years, sperm concentration has fallen about 50% around the world,” said senior study author Melissa Perry, dean of the College of Public Health at George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia.
“What is not known is the culprit,” Perry said. “While there are likely many more contributing causes, our study demonstrates a strong association between two common insecticides —organophosphates and N-methyl carbamates — and the decline of sperm concentration.”
https://us.cnn.com/2023/11/15/health...ess/index.html
Pesticides used in our homes, gardens and lawns and sprayed on foods we eat are contributing to a dramatic decline in sperm count among men worldwide, according to a new analysis of studies over the last 50 years.
“Over the course of 50 years, sperm concentration has fallen about 50% around the world,” said senior study author Melissa Perry, dean of the College of Public Health at George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia.
“What is not known is the culprit,” Perry said. “While there are likely many more contributing causes, our study demonstrates a strong association between two common insecticides —organophosphates and N-methyl carbamates — and the decline of sperm concentration.”
https://us.cnn.com/2023/11/15/health...ess/index.html
The “Self-Driving Lab” That Unlocks Quantum Dot Secrets in Hours – Instead of Years
Researchers have developed SmartDope, an autonomous system capable of rapidly identifying the best materials for electronic and photonic devices, addressing a longstanding challenge in quantum dot synthesis. SmartDope operates as a self-driving lab, conducting experiments in a continuous flow reactor and utilizing machine learning to optimize quantum dot production. In just one day, it surpassed the previous quantum yield record, showcasing the potential of self-driving labs for accelerating material science. ... It can take years of focused laboratory work to determine how to make the highest quality materials for use in electronic and photonic devices. Researchers have now developed an autonomous system that can identify how to synthesize “best-in-class” materials for specific applications in hours or days.
... The SmartDope system is a “self-driving” lab. ... Once it has received that initial information, SmartDope begins running experiments autonomously. The experiments are conducted in a continuous flow reactor that uses extremely small amounts of chemicals to conduct quantum dot synthesis experiments rapidly as the precursors flow through the system and react with each other. ...
https://scitechdaily.com/smartdope-t...tead-of-years/
Researchers have developed SmartDope, an autonomous system capable of rapidly identifying the best materials for electronic and photonic devices, addressing a longstanding challenge in quantum dot synthesis. SmartDope operates as a self-driving lab, conducting experiments in a continuous flow reactor and utilizing machine learning to optimize quantum dot production. In just one day, it surpassed the previous quantum yield record, showcasing the potential of self-driving labs for accelerating material science. ... It can take years of focused laboratory work to determine how to make the highest quality materials for use in electronic and photonic devices. Researchers have now developed an autonomous system that can identify how to synthesize “best-in-class” materials for specific applications in hours or days.
... The SmartDope system is a “self-driving” lab. ... Once it has received that initial information, SmartDope begins running experiments autonomously. The experiments are conducted in a continuous flow reactor that uses extremely small amounts of chemicals to conduct quantum dot synthesis experiments rapidly as the precursors flow through the system and react with each other. ...
https://scitechdaily.com/smartdope-t...tead-of-years/
A Milestone in Computing: 2D In-Memory Processor With Over 1000 Transistors
EPFL researchers have created an energy-efficient in-memory processor using MoS2, combining over 1000 transistors. This processor, which efficiently performs vector-matrix multiplication, represents a shift away from traditional von Neumann architecture and could boost the European semiconductor industry.
https://scitechdaily.com/a-milestone...0-transistors/
EPFL researchers have created an energy-efficient in-memory processor using MoS2, combining over 1000 transistors. This processor, which efficiently performs vector-matrix multiplication, represents a shift away from traditional von Neumann architecture and could boost the European semiconductor industry.
https://scitechdaily.com/a-milestone...0-transistors/
New Study Decodes Pareidolia in 40,000-Year-Old Cave Paintings
New suggests that Ice Age cave art was partly influenced by pareidolia, a phenomenon where humans see meaningful shapes in random patterns. Focusing on caves in Northern Spain, the study found that many images incorporated natural features of the cave walls, indicating that artists were influenced by both pareidolia and their creativity.

... Top image: Upper Palaeolithic drawing of the partial outline of a horse that uses the natural edge of the cave wall to represent the back and head of the horse. Bottom image: The same horse drawing under the simulated VR light conditions. ...
New suggests that Ice Age cave art was partly influenced by pareidolia, a phenomenon where humans see meaningful shapes in random patterns. Focusing on caves in Northern Spain, the study found that many images incorporated natural features of the cave walls, indicating that artists were influenced by both pareidolia and their creativity.

... Top image: Upper Palaeolithic drawing of the partial outline of a horse that uses the natural edge of the cave wall to represent the back and head of the horse. Bottom image: The same horse drawing under the simulated VR light conditions. ...
Americans’ trust in science declining, Pew survey says
mericans’ trust in science and scientists has dropped since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, according to a new report by Pew Research Center.
The percent of American adults who say science has a “mostly positive” effect on society fell to 57%, down 8 percentage points since November 2021 and 16 percentage points since just before the pandemic, according to the survey of more than 8,800 U.S. adults conducted in the last week of September. More than a third of respondents believed that the impact of science has been equally positive and negative, while 8% think science has a “mostly negative” impact on society.
... Trust in science wasn’t the same across the political spectrum: The Pew survey found that Republicans had less confidence in scientists and the benefits of science than Democrats. Less than half of Republicans (47%) said science has had a mostly positive effect on society, a decline from 70% in 2019. Sixty-nine percent of Democrats say science has had a mostly positive effect on society, although that has also declined by 8 points from 2019. ...
... Despite public opinion turning away from science, nearly three-quarters of U.S. adults expressed confidence in scientists to act in the public’s best interest. More Americans had at least some faith in scientists to act in the public’s best interest than other prominent groups, such as business leaders, religious leaders, journalists and elected officials. ...
... Wallace attributes the rise of scientific mistrust to what she described as an “infodemic” about Covid-19: an influx of conflicting information and opinions about the virus and prevention measures.
“It led to a lot of public chaos, bewilderment, message fatigue and people just kind of checking out,” Wallace told CNN. “It just causes a lot of confusion because we have different people with big platforms saying different things.” ... “Everyone was at home on social media and interacting in these echo chambers filtering out any information they didn’t want to see,” Wallace said. “Different groups come to different conclusions because they’re interacting with different information.”
And often, experts say, that flood of false information was intentional and malicious — attacking scientific voices in favor of inaccurate content.
Dr. Peter Hotez, the dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, said a “revisionist history” popped up as the pandemic emerged, blaming scientists for seeding mistrust and exacerbating the harms of Covid-19.
mericans’ trust in science and scientists has dropped since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, according to a new report by Pew Research Center.
The percent of American adults who say science has a “mostly positive” effect on society fell to 57%, down 8 percentage points since November 2021 and 16 percentage points since just before the pandemic, according to the survey of more than 8,800 U.S. adults conducted in the last week of September. More than a third of respondents believed that the impact of science has been equally positive and negative, while 8% think science has a “mostly negative” impact on society.
... Trust in science wasn’t the same across the political spectrum: The Pew survey found that Republicans had less confidence in scientists and the benefits of science than Democrats. Less than half of Republicans (47%) said science has had a mostly positive effect on society, a decline from 70% in 2019. Sixty-nine percent of Democrats say science has had a mostly positive effect on society, although that has also declined by 8 points from 2019. ...
... Despite public opinion turning away from science, nearly three-quarters of U.S. adults expressed confidence in scientists to act in the public’s best interest. More Americans had at least some faith in scientists to act in the public’s best interest than other prominent groups, such as business leaders, religious leaders, journalists and elected officials. ...
... Wallace attributes the rise of scientific mistrust to what she described as an “infodemic” about Covid-19: an influx of conflicting information and opinions about the virus and prevention measures.
“It led to a lot of public chaos, bewilderment, message fatigue and people just kind of checking out,” Wallace told CNN. “It just causes a lot of confusion because we have different people with big platforms saying different things.” ... “Everyone was at home on social media and interacting in these echo chambers filtering out any information they didn’t want to see,” Wallace said. “Different groups come to different conclusions because they’re interacting with different information.”
And often, experts say, that flood of false information was intentional and malicious — attacking scientific voices in favor of inaccurate content.
Dr. Peter Hotez, the dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, said a “revisionist history” popped up as the pandemic emerged, blaming scientists for seeding mistrust and exacerbating the harms of Covid-19.
stlah
















Comment