Start packing, we only have 250 million years more. But, I suspect, we won't be on the planet by then, or will find a way to fine tune the sun and volcanoes. 250 million years is a long time, after all ...
But in the shorter term, although we won't be wiped out as a species, still great concerns ...
In happier news, we are slowly getting ready for that jump to the stars ...
(Just a little note that the Japanese Space Agency, JAXA, already accomplished this a couple of years ago, so this is only a milestone for NASA ... )
NASA is also making waves here ...
And more music of the spheres ...
Merging Black Holes ...
A possible hint of life in Europe ... I mean, on "Europa" ...
Building blocks in deep space too ...
And more ways to look into space are coming ...
Now, from the very vast to the very small ...
No antimatter anti-gravity levitation! There goes my anti-matter hoverboard! 
Maybe genetics can help us adapt to the new super hot super-continent??
It is sometime good to marry your cousin ...
Well, we can't survive the hot age, but got through the ice age ...
Mysteries and discoveries still remain right here on earth ...
We won't need sex soon ... or, on the brighter side, anyone soon can have a child ... fairly soon, anyway ...
Maybe after the mammals are gone, AI will replace us ... or figure out how to save us ...
And getting smarter ...
But the humans are still ahead ... for now ...
AI is already doing so good things, however imperfectly ...
This is AI HUGE!
AI can often more understanding of human behavior and movement ...
But AI can also track and spy on us in other ways ...
AI and automation might help places like Japan with a labor shortage, but also unemployment caused by AI!!! 
Hopefully, we will regulate AI better than the internet ... doubtful ...
Maybe we will handle AI better than atomic weaponry ... which, sadly, is far from over ...
Gassho, J
stlah
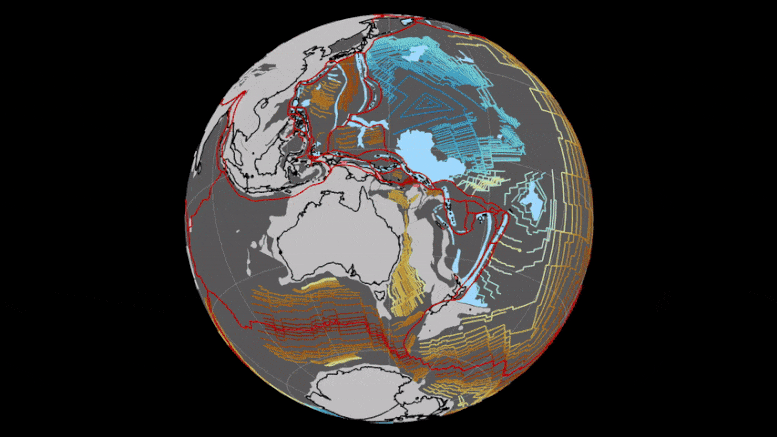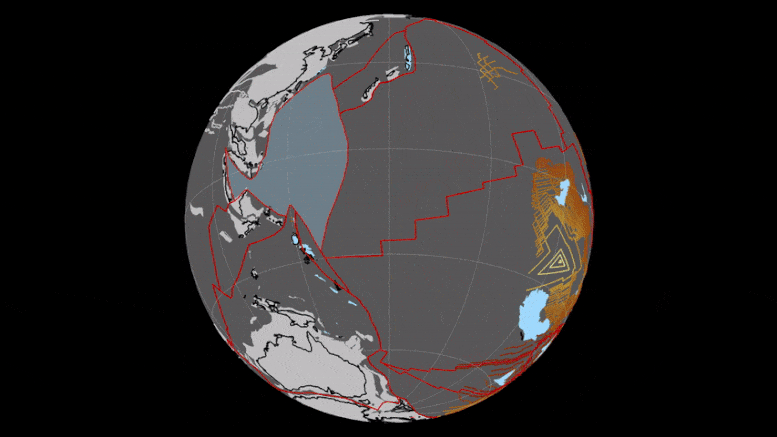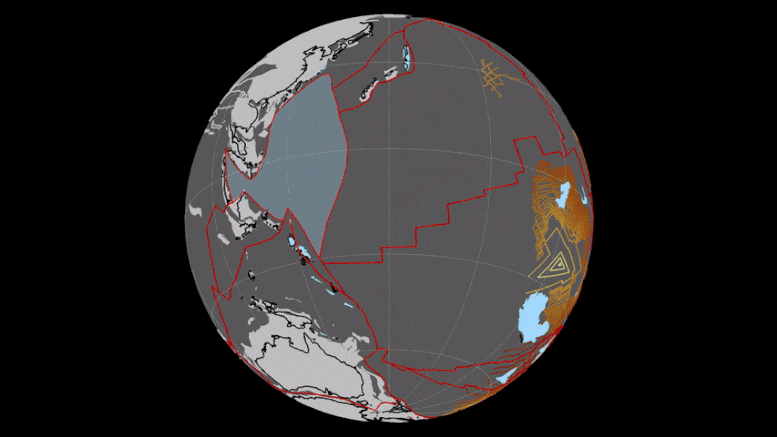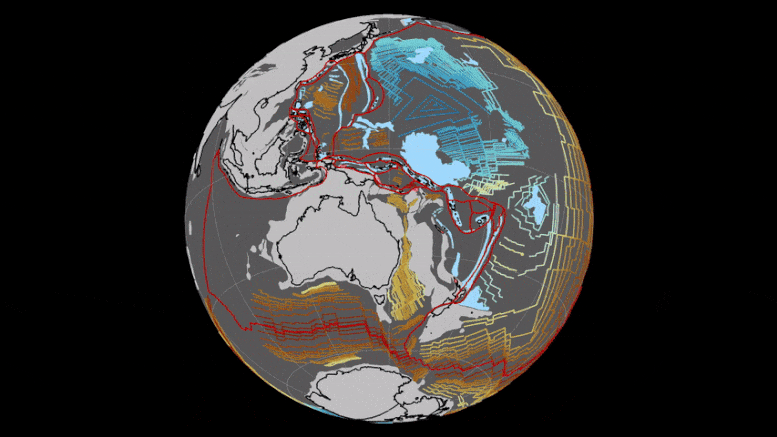
A study predicts a mass extinction of mammals in 250 million years due to extreme heat from the formation of a supercontinent.
The research highlights the lethal combination of a hotter sun, increased CO2, and continental effects, underscoring the importance of landmass layouts in evaluating the habitability of exoplanets.
Unprecedented heat is likely to lead to the next mass extinction since the dinosaurs died out, eliminating nearly all mammals in some 250 million years’ time, according to a new study.
The research, published on September 25 in the journal Nature Geoscience and led by the University of Bristol, presents the first-ever supercomputer climate models of the distant future and demonstrates how climate extremes will dramatically intensify when the world’s continents eventually merge to form one hot, dry and largely uninhabitable supercontinent.
The findings project how these high temperatures are set to further increase, as the sun becomes brighter, emitting more energy and warming the Earth. Tectonic processes, occurring in the Earth’s crust and resulting in supercontinent formation would also lead to more frequent volcanic eruptions which produce huge releases of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, further warming the planet.
Mammals, including humans, have survived historically thanks to their ability to adjust to weather extremes, especially through adaptations such as fur and hibernating in the cold, as well as short spells of warm weather hibernation.
While mammals have evolved to lower their cold temperature survivable limit, their upper-temperature tolerance has generally remained constant. This makes exposure to prolonged excessive heat much harder to overcome and the climate simulations, if realized, would ultimately prove unsurvivable.
BELOW: This image shows the geography of today's Earth and the projected geography of Earth in 250 million years, when all the continents converge into one supercontinent

and
https://us.cnn.com/2023/09/26/world/...scn/index.html
The research highlights the lethal combination of a hotter sun, increased CO2, and continental effects, underscoring the importance of landmass layouts in evaluating the habitability of exoplanets.
Unprecedented heat is likely to lead to the next mass extinction since the dinosaurs died out, eliminating nearly all mammals in some 250 million years’ time, according to a new study.
The research, published on September 25 in the journal Nature Geoscience and led by the University of Bristol, presents the first-ever supercomputer climate models of the distant future and demonstrates how climate extremes will dramatically intensify when the world’s continents eventually merge to form one hot, dry and largely uninhabitable supercontinent.
The findings project how these high temperatures are set to further increase, as the sun becomes brighter, emitting more energy and warming the Earth. Tectonic processes, occurring in the Earth’s crust and resulting in supercontinent formation would also lead to more frequent volcanic eruptions which produce huge releases of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, further warming the planet.
Mammals, including humans, have survived historically thanks to their ability to adjust to weather extremes, especially through adaptations such as fur and hibernating in the cold, as well as short spells of warm weather hibernation.
While mammals have evolved to lower their cold temperature survivable limit, their upper-temperature tolerance has generally remained constant. This makes exposure to prolonged excessive heat much harder to overcome and the climate simulations, if realized, would ultimately prove unsurvivable.
BELOW: This image shows the geography of today's Earth and the projected geography of Earth in 250 million years, when all the continents converge into one supercontinent

and
https://us.cnn.com/2023/09/26/world/...scn/index.html
Breaching the Limit: Global Concerns Rise As Six Key Planetary Boundaries Are Exceeded
A new study updates the planetary boundary framework and shows human activities are increasingly impacting the planet and, thereby, increasing the risk of triggering dramatic changes in overall Earth conditions.
For over 3 billion years, the interaction between life (represented by the planetary boundary, Biosphere Integrity) and climate have controlled the overall environmental conditions on Earth. Human activities, for example replacing nature with other land uses, changing the amount of water in rivers and in soil, the introduction of synthetic chemicals to the open environment, and the emission of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere all influence these interactions. ... The nine “planetary boundaries” represent components of the global environment that regulate the stability and liveability of the planet for people. The degree of breaching of the safe boundary levels is caused by human-driven activities impacting the components. The planetary boundaries framework applies the newest scientific understanding of the functioning of the Earth system to identify a ”safe operating space” for humanity by proposing limits for the extent to which human activities can be allowed to impact critical processes without risk of potentially triggering irreversible changes in the Earth conditions that support us.
... “Crossing six boundaries in itself does not necessarily imply a disaster will ensue but it is a clear warning signal. We can regard it as we do our own blood pressure. A BP over 120/80 is not a guarantee of a heart attack but it increases the risk of one. Therefore, we try to bring it down. For our own – and our children’s – sakes we need to reduce the pressure on these six planetary boundaries.” ...

https://scitechdaily.com/breaching-t...-are-exceeded/
A new study updates the planetary boundary framework and shows human activities are increasingly impacting the planet and, thereby, increasing the risk of triggering dramatic changes in overall Earth conditions.
For over 3 billion years, the interaction between life (represented by the planetary boundary, Biosphere Integrity) and climate have controlled the overall environmental conditions on Earth. Human activities, for example replacing nature with other land uses, changing the amount of water in rivers and in soil, the introduction of synthetic chemicals to the open environment, and the emission of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere all influence these interactions. ... The nine “planetary boundaries” represent components of the global environment that regulate the stability and liveability of the planet for people. The degree of breaching of the safe boundary levels is caused by human-driven activities impacting the components. The planetary boundaries framework applies the newest scientific understanding of the functioning of the Earth system to identify a ”safe operating space” for humanity by proposing limits for the extent to which human activities can be allowed to impact critical processes without risk of potentially triggering irreversible changes in the Earth conditions that support us.
... “Crossing six boundaries in itself does not necessarily imply a disaster will ensue but it is a clear warning signal. We can regard it as we do our own blood pressure. A BP over 120/80 is not a guarantee of a heart attack but it increases the risk of one. Therefore, we try to bring it down. For our own – and our children’s – sakes we need to reduce the pressure on these six planetary boundaries.” ...

https://scitechdaily.com/breaching-t...-are-exceeded/
(Just a little note that the Japanese Space Agency, JAXA, already accomplished this a couple of years ago, so this is only a milestone for NASA ... )

Astrophysicist explains why NASA milestone is 'incredible'
NASA returned its first ever asteroid sample to Earth seven years after launching into space. The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft flew by Earth to deliver the pristine sample from the near-Earth asteroid Bennu.
More here: https://www.npr.org/2023/09/24/12013...-back-to-earth

NASA returned its first ever asteroid sample to Earth seven years after launching into space. The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft flew by Earth to deliver the pristine sample from the near-Earth asteroid Bennu.
More here: https://www.npr.org/2023/09/24/12013...-back-to-earth

NASA’s Cosmic Vision: Simulating Our Galaxy Through Gravitational Waves
Using simulated data, astronomers have depicted the sky through gravitational waves, revealing the need for space observatories to detect binary systems. Future projects like LISA aim to uncover thousands of these hard-to-detect systems, marking a paradigm shift in space observation. (Artist’s illustration — see video below for simulation.)
Astronomers using simulated data have produced a glimpse of the sky as it would appear in gravitational waves, cosmic ripples in space-time generated by orbiting objects. The image shows how space-based gravitational wave observatories expected to launch in the next decade will enhance our understanding of our galactic home.
BELOW: Watch as gravitational waves from a simulated population of compact binary systems combine into a synthetic map of the entire sky. Such systems contain white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes in tight orbits. Maps like this using real data will be possible once space-based gravitational wave observatories become active in the next decade. Brighter spots indicate sources with stronger signals and lighter colors indicate those with higher frequencies. Larger colored patches show sources whose positions are less well known. The inset shows the frequency and strength of the gravitational signal, as well as the sensitivity limit for LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna), an observatory now being designed by ESA (European Space Agency) in collaboration with NASA for launch in the 2030s. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
https://scitechdaily.com/nasas-cosmi...ational-waves/
Using simulated data, astronomers have depicted the sky through gravitational waves, revealing the need for space observatories to detect binary systems. Future projects like LISA aim to uncover thousands of these hard-to-detect systems, marking a paradigm shift in space observation. (Artist’s illustration — see video below for simulation.)
Astronomers using simulated data have produced a glimpse of the sky as it would appear in gravitational waves, cosmic ripples in space-time generated by orbiting objects. The image shows how space-based gravitational wave observatories expected to launch in the next decade will enhance our understanding of our galactic home.
BELOW: Watch as gravitational waves from a simulated population of compact binary systems combine into a synthetic map of the entire sky. Such systems contain white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes in tight orbits. Maps like this using real data will be possible once space-based gravitational wave observatories become active in the next decade. Brighter spots indicate sources with stronger signals and lighter colors indicate those with higher frequencies. Larger colored patches show sources whose positions are less well known. The inset shows the frequency and strength of the gravitational signal, as well as the sensitivity limit for LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna), an observatory now being designed by ESA (European Space Agency) in collaboration with NASA for launch in the 2030s. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
https://scitechdaily.com/nasas-cosmi...ational-waves/
Stellar Concert: Astronomers Tune In to the Sounds of Twinkling Stars
Northwestern University scientists have developed the first 3D simulations to study the energy rippling from a massive star’s core to its outer surface, providing new insights into stars’ inherent ‘twinkle’.
The team also converted these waves into sound, enabling listeners to ‘hear’ the inside of a star and its natural twinkle.
Northwestern University scientists have developed the first 3D simulations to study the energy rippling from a massive star’s core to its outer surface, providing new insights into stars’ inherent ‘twinkle’.
The team also converted these waves into sound, enabling listeners to ‘hear’ the inside of a star and its natural twinkle.
Using new simulation technology, scientists predict the existence of massive merging black holes in Milky Way-like galaxies, challenging established theories.
... Stellar-mass black holes are celestial objects born from the collapse of stars with masses of a few to low hundreds of times that of our sun. Their gravitational field is so intense that neither matter nor radiation can evade them, making their detection exceedingly difficult. Therefore, when the tiny ripples in spacetime produced by the merger of two black holes were detected in 2015, by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO), it was hailed as a watershed moment. According to astrophysicists, the two merging black holes at the origin of the signal were about 30 times the mass of the sun and located 1.5 billion light-years away. What mechanisms produce these black holes? Are they the product of the evolution of two stars, similar to our sun but significantly more massive, evolving within a binary system? Or do they result from black holes in densely populated star clusters running into each other by chance? Or might a more exotic mechanism be involved? All of these questions are still hotly debated today.
... “Models prior to POSYDON predicted a negligible formation rate of merging binary black holes in galaxies similar to the Milky Way, and they particularly did not anticipate the existence of merging black holes as massive as 30 times the mass of our sun. POSYDON has demonstrated that such massive black holes might exist in Milky Way-like galaxies” ...
https://scitechdaily.com/challenging...f-black-holes/
... Stellar-mass black holes are celestial objects born from the collapse of stars with masses of a few to low hundreds of times that of our sun. Their gravitational field is so intense that neither matter nor radiation can evade them, making their detection exceedingly difficult. Therefore, when the tiny ripples in spacetime produced by the merger of two black holes were detected in 2015, by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO), it was hailed as a watershed moment. According to astrophysicists, the two merging black holes at the origin of the signal were about 30 times the mass of the sun and located 1.5 billion light-years away. What mechanisms produce these black holes? Are they the product of the evolution of two stars, similar to our sun but significantly more massive, evolving within a binary system? Or do they result from black holes in densely populated star clusters running into each other by chance? Or might a more exotic mechanism be involved? All of these questions are still hotly debated today.
... “Models prior to POSYDON predicted a negligible formation rate of merging binary black holes in galaxies similar to the Milky Way, and they particularly did not anticipate the existence of merging black holes as massive as 30 times the mass of our sun. POSYDON has demonstrated that such massive black holes might exist in Milky Way-like galaxies” ...
https://scitechdaily.com/challenging...f-black-holes/
Webb spots a building block of life on Jupiter’s moon Europa
Two independent teams of astronomers used the James Webb Space Telescope to observe the frozen surface of Europa, and each analysis of the space observatory’s detections revealed an abundance of carbon dioxide within a specific region of the frigid terrain. Both studies describing the findings were published September 21 in the journal Science. ... Europa is one of several ocean worlds in our solar system besides Earth where scientists believe life could exist. Beneath a thick ice shell, Europa harbors a subsurface global ocean that may contain twice as much water as our planet’s oceans.
But environments suitable for life need more than water — they also require a supply of organic molecules and an energy source, according to NASA. “We now think that we have observational evidence that the carbon we see on Europa’s surface came from the ocean. That’s not a trivial thing. Carbon is a biologically essential element,” said Samantha Trumbo, lead author of the second study and a 51 Pegasi B Fellow at Cornell University, in a statement. Scientists have long questioned whether Europa’s ocean contained carbon and other chemicals necessary for life. ...
https://us.cnn.com/2023/09/27/world/...scn/index.html
Two independent teams of astronomers used the James Webb Space Telescope to observe the frozen surface of Europa, and each analysis of the space observatory’s detections revealed an abundance of carbon dioxide within a specific region of the frigid terrain. Both studies describing the findings were published September 21 in the journal Science. ... Europa is one of several ocean worlds in our solar system besides Earth where scientists believe life could exist. Beneath a thick ice shell, Europa harbors a subsurface global ocean that may contain twice as much water as our planet’s oceans.
But environments suitable for life need more than water — they also require a supply of organic molecules and an energy source, according to NASA. “We now think that we have observational evidence that the carbon we see on Europa’s surface came from the ocean. That’s not a trivial thing. Carbon is a biologically essential element,” said Samantha Trumbo, lead author of the second study and a 51 Pegasi B Fellow at Cornell University, in a statement. Scientists have long questioned whether Europa’s ocean contained carbon and other chemicals necessary for life. ...
https://us.cnn.com/2023/09/27/world/...scn/index.html
Never Before Detected – Organic Molecule Essential for Life Found in Interstellar Space
Tryptophan is among the 20 vital amino acids necessary for protein synthesis, crucial for life’s evolution on Earth. This amino acid has many spectral features in the infrared, as had been previously characterized by Susana Iglesias Groth, an IAC researcher.
Utilizing data from the Spitzer Space Observatory, she identified over 10 emission bands for this molecule, the strongest according to her laboratory measurements. ... The study presents evidence that tryptophan-associated emission lines may also be present in other star-forming regions and suggests that its presence, and possibly that of other amino acids, is common in the gas from which stars and planets form. “It is likely that amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, may be enriching the gas in the protoplanetary discs and atmospheres of young, newly formed exoplanets and perhaps accelerating the emergence of life there,” says Iglesias-Groth. ...
... “It is well known that amino acids are part of meteorites and may have been present as early as the formation of the Solar System” explains Iglesias-Groth. “The discovery of tryptophan and, hopefully, of other amino acids in the future, could indicate that protein-building agents, which are key to the development of living organisms, exist naturally in the regions where stars and planetary systems form, and that life may be more common in our Galaxy than we could have predicted” she concludes ...

https://scitechdaily.com/never-befor...stellar-space/
Tryptophan is among the 20 vital amino acids necessary for protein synthesis, crucial for life’s evolution on Earth. This amino acid has many spectral features in the infrared, as had been previously characterized by Susana Iglesias Groth, an IAC researcher.
Utilizing data from the Spitzer Space Observatory, she identified over 10 emission bands for this molecule, the strongest according to her laboratory measurements. ... The study presents evidence that tryptophan-associated emission lines may also be present in other star-forming regions and suggests that its presence, and possibly that of other amino acids, is common in the gas from which stars and planets form. “It is likely that amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, may be enriching the gas in the protoplanetary discs and atmospheres of young, newly formed exoplanets and perhaps accelerating the emergence of life there,” says Iglesias-Groth. ...
... “It is well known that amino acids are part of meteorites and may have been present as early as the formation of the Solar System” explains Iglesias-Groth. “The discovery of tryptophan and, hopefully, of other amino acids in the future, could indicate that protein-building agents, which are key to the development of living organisms, exist naturally in the regions where stars and planetary systems form, and that life may be more common in our Galaxy than we could have predicted” she concludes ...

https://scitechdaily.com/never-befor...stellar-space/
Constructing the World’s Largest Optics: The Giant Magellan Telescope’s Final Mirror Fabrication Begins
The Giant Magellan Telescope is finalizing its last primary mirror, with the goal to surpass current space telescopes in sensitivity and resolution. ... Together, the mirrors will collect more light than any other telescope in existence, allowing humanity to unlock the secrets of the Universe by providing detailed chemical analyses of celestial objects and their origin. ...
... Last week, the University of Arizona Richard F. Caris Mirror Lab closed the lid on nearly 20 tons of the purest optical glass inside a one-of-a-kind oven housed beneath the stands of the Arizona Wildcats Football Stadium. The spinning oven will heat the glass to 1,165°C (2,129°F) so as it melts, it is forced outward to form the mirror’s curved paraboloid surface. Measuring 8.4 meters (26.7 feet) in diameter—about two stories tall when standing on edge—the mirror will cool over the next three months before moving into the polishing stage.
https://scitechdaily.com/constructin...cation-begins/
The Giant Magellan Telescope is finalizing its last primary mirror, with the goal to surpass current space telescopes in sensitivity and resolution. ... Together, the mirrors will collect more light than any other telescope in existence, allowing humanity to unlock the secrets of the Universe by providing detailed chemical analyses of celestial objects and their origin. ...
... Last week, the University of Arizona Richard F. Caris Mirror Lab closed the lid on nearly 20 tons of the purest optical glass inside a one-of-a-kind oven housed beneath the stands of the Arizona Wildcats Football Stadium. The spinning oven will heat the glass to 1,165°C (2,129°F) so as it melts, it is forced outward to form the mirror’s curved paraboloid surface. Measuring 8.4 meters (26.7 feet) in diameter—about two stories tall when standing on edge—the mirror will cool over the next three months before moving into the polishing stage.
https://scitechdaily.com/constructin...cation-begins/
Unveiling the Quantum World: Scientists Capture Quantum Entanglement of Photons in Real-Time
Researchers have pioneered a technique for swiftly and efficiently reconstructing the full quantum state of entangled particles, utilizing advanced camera technology to visualize the wave function of two entangled photons in real time. The innovative method is exponentially faster than previous ones, taking minutes or seconds instead of days, and holds the potential for advancing quantum technology by enhancing quantum state characterization, quantum communication, and quantum imaging techniques.
https://scitechdaily.com/unveiling-t...-in-real-time/
Researchers have pioneered a technique for swiftly and efficiently reconstructing the full quantum state of entangled particles, utilizing advanced camera technology to visualize the wave function of two entangled photons in real time. The innovative method is exponentially faster than previous ones, taking minutes or seconds instead of days, and holds the potential for advancing quantum technology by enhancing quantum state characterization, quantum communication, and quantum imaging techniques.
https://scitechdaily.com/unveiling-t...-in-real-time/

Antimatter Levitation Debunked: Groundbreaking CERN Experiment Reveals Gravity’s Pull on Antihydrogen
An experiment by the ALPHA collaboration at CERN has shown that antihydrogen, a combination of an anti-proton and an antielectron, is pulled downward by gravity, dispelling the idea of antigravity for antimatter. This aligns with Einstein’s general relativity theory, which predates antimatter’s discovery and suggests that all matter, regular or anti, reacts identically to gravitational forces.
... “The bottom line is that there’s no free lunch, and we’re not going to be able to levitate using antimatter.” ...
... Nevertheless, the idea that antimatter and matter might be affected differently by gravity was enticing because it could potentially explain some cosmic conundrums. For example, it could have led to the spatial separation of matter and antimatter in the early universe, explaining why we see only a small amount of antimatter in the universe around us. Most theories predict that equal amounts of matter and antimatter should have been produced during the Big Bang that birthed the universe. ...
An experiment by the ALPHA collaboration at CERN has shown that antihydrogen, a combination of an anti-proton and an antielectron, is pulled downward by gravity, dispelling the idea of antigravity for antimatter. This aligns with Einstein’s general relativity theory, which predates antimatter’s discovery and suggests that all matter, regular or anti, reacts identically to gravitational forces.
... “The bottom line is that there’s no free lunch, and we’re not going to be able to levitate using antimatter.” ...
... Nevertheless, the idea that antimatter and matter might be affected differently by gravity was enticing because it could potentially explain some cosmic conundrums. For example, it could have led to the spatial separation of matter and antimatter in the early universe, explaining why we see only a small amount of antimatter in the universe around us. Most theories predict that equal amounts of matter and antimatter should have been produced during the Big Bang that birthed the universe. ...
Scientists Successfully Genetically Modify Individual Cells in Living Animals
Researchers have developed a technique using CRISPR-Cas to simultaneously modify multiple genes in the cells of adult animals, creating a mosaic-like pattern that simplifies studying genetic diseases. This approach has uncovered new insights into the genetic disorder 22q11.2 deletion syndrome and holds the potential to decrease the number of animal experiments in the future. Credit: ETH Zurich
One proven method for tracking down the genetic origins of diseases is to knock out a single gene in animals and study the consequences this has for the organism. The problem is that for many diseases, the pathology is determined by multiple genes, complicating the task for scientists trying to pinpoint the contribution of any single gene to the condition. To do this, they would have to perform many animal experiments – one for each desired gene modification.
Researchers led by Randall Platt, Professor of Biological Engineering at the Department of Biosystems Science and Engineering at ETH Zurich in Basel, have now developed a method that will greatly simplify and speed up research with laboratory animals: using the CRISPR-Cas gene scissors, they simultaneously make several dozen gene changes in the cells of a single animal, much like a mosaic.
While no more than one gene is altered in each cell, the various cells within an organ are altered in different ways. Individual cells can then be precisely analyzed. This enables researchers to study the ramifications of many different gene changes in a single experiment.
https://scitechdaily.com/scientists-...iving-animals/
Researchers have developed a technique using CRISPR-Cas to simultaneously modify multiple genes in the cells of adult animals, creating a mosaic-like pattern that simplifies studying genetic diseases. This approach has uncovered new insights into the genetic disorder 22q11.2 deletion syndrome and holds the potential to decrease the number of animal experiments in the future. Credit: ETH Zurich
One proven method for tracking down the genetic origins of diseases is to knock out a single gene in animals and study the consequences this has for the organism. The problem is that for many diseases, the pathology is determined by multiple genes, complicating the task for scientists trying to pinpoint the contribution of any single gene to the condition. To do this, they would have to perform many animal experiments – one for each desired gene modification.
Researchers led by Randall Platt, Professor of Biological Engineering at the Department of Biosystems Science and Engineering at ETH Zurich in Basel, have now developed a method that will greatly simplify and speed up research with laboratory animals: using the CRISPR-Cas gene scissors, they simultaneously make several dozen gene changes in the cells of a single animal, much like a mosaic.
While no more than one gene is altered in each cell, the various cells within an organ are altered in different ways. Individual cells can then be precisely analyzed. This enables researchers to study the ramifications of many different gene changes in a single experiment.
https://scitechdaily.com/scientists-...iving-animals/
A Genetic Paradox: Inbreeding Can Be Beneficial in the Long Run
Despite the challenges of inbreeding and limited genetic diversity, the Svalbard reindeer have remarkably adapted to harsh living conditions in an extraordinarily short period, a situation researchers term a genetic paradox. However, the question remains: can they withstand the impacts of climate change?
... Evolutionary theory suggests this is a poor starting point since inbreeding can quickly lead to an accumulation of harmful mutations and genetic variants followed by disease and death. But this has not prevented the Svalbard reindeer from evolving into what is today a viable population of more than 20,000 animals. “Despite the low genetic diversity, they have managed to develop a number of adaptations to life in the High Arctic. They are, for example, smaller in size and have shorter legs than other northern reindeer and caribou subspecies,” says Dussex. ... “In this case, we are dealing with a population that suffers from a high degree of inbreeding, which is usually bad news for a small population. But inbreeding can also help a population to get rid of harmful mutations, a phenomenon technically called ‘purging’,” says Martin. ...
[But] It is far from certain that the Svalbard reindeer will be able to adapt as well to the rapid changes that result from global warming. The adaptations the reindeer have developed for the extreme arctic climate may fall short as the archipelago is now rapidly warming, which is changing both snow cover and vegetation. ...
https://scitechdaily.com/a-genetic-p...-the-long-run/
Despite the challenges of inbreeding and limited genetic diversity, the Svalbard reindeer have remarkably adapted to harsh living conditions in an extraordinarily short period, a situation researchers term a genetic paradox. However, the question remains: can they withstand the impacts of climate change?
... Evolutionary theory suggests this is a poor starting point since inbreeding can quickly lead to an accumulation of harmful mutations and genetic variants followed by disease and death. But this has not prevented the Svalbard reindeer from evolving into what is today a viable population of more than 20,000 animals. “Despite the low genetic diversity, they have managed to develop a number of adaptations to life in the High Arctic. They are, for example, smaller in size and have shorter legs than other northern reindeer and caribou subspecies,” says Dussex. ... “In this case, we are dealing with a population that suffers from a high degree of inbreeding, which is usually bad news for a small population. But inbreeding can also help a population to get rid of harmful mutations, a phenomenon technically called ‘purging’,” says Martin. ...
[But] It is far from certain that the Svalbard reindeer will be able to adapt as well to the rapid changes that result from global warming. The adaptations the reindeer have developed for the extreme arctic climate may fall short as the archipelago is now rapidly warming, which is changing both snow cover and vegetation. ...
https://scitechdaily.com/a-genetic-p...-the-long-run/
Unraveling an Ice Age Mystery – New Study Reveals Surprises About Early Human Migration
A recent study analyzed pollen data around Lake Baikal in Siberia to uncover details about early human migration across Europe and Asia 45,000-50,000 years ago. The evidence suggests that warming temperatures supported expanding forests, facilitating human migration into Siberia, and contradicting some previous archaeological perspectives.
... the pollen data suggest that the dispersal of people occurred during some of the highest temperatures in the late Pleistocene, which also would have featured higher humidity. The ancient pollen record shows coniferous forests and grasslands characterized the region, able to support foraging and hunting by humans. Goebel said the environmental data, combined with archeological evidence, tell a new story.
“This contradicts some recent archaeological perspectives in Europe,” said the KU researcher. “The key factor here is accurate dating, not just of human fossils and animal bones associated with the archaeology of these people, but also of environmental records, including from pollen. What we have presented is a robust chronology of environmental changes in Lake Baikal during this time period, complemented by a well-dated archaeological record of Homo sapiens’ presence in the region.” ...
BELOW: Map showing theorized migration routes of early Homo sapiens from Africa across Eurasia.

https://scitechdaily.com/unraveling-...man-migration/
A recent study analyzed pollen data around Lake Baikal in Siberia to uncover details about early human migration across Europe and Asia 45,000-50,000 years ago. The evidence suggests that warming temperatures supported expanding forests, facilitating human migration into Siberia, and contradicting some previous archaeological perspectives.
... the pollen data suggest that the dispersal of people occurred during some of the highest temperatures in the late Pleistocene, which also would have featured higher humidity. The ancient pollen record shows coniferous forests and grasslands characterized the region, able to support foraging and hunting by humans. Goebel said the environmental data, combined with archeological evidence, tell a new story.
“This contradicts some recent archaeological perspectives in Europe,” said the KU researcher. “The key factor here is accurate dating, not just of human fossils and animal bones associated with the archaeology of these people, but also of environmental records, including from pollen. What we have presented is a robust chronology of environmental changes in Lake Baikal during this time period, complemented by a well-dated archaeological record of Homo sapiens’ presence in the region.” ...
BELOW: Map showing theorized migration routes of early Homo sapiens from Africa across Eurasia.

https://scitechdaily.com/unraveling-...man-migration/
Scientists Discover New Insect Genus in Peruvian Rainforest
Capitojoppa amazonica is a large parasitoid wasp species that has only been discovered in the Allpahuyao-Mishana National Reserve in the Peruvian Amazon. Here, the wasp is photographed from the front.

https://scitechdaily.com/scientists-...an-rainforest/
Capitojoppa amazonica is a large parasitoid wasp species that has only been discovered in the Allpahuyao-Mishana National Reserve in the Peruvian Amazon. Here, the wasp is photographed from the front.

https://scitechdaily.com/scientists-...an-rainforest/
Japanese scientists race to create human eggs and sperm in the lab
... Hayashi, a developmental geneticist at Osaka University in Japan, is a pioneer in one of the most exciting — and controversial — fields of biomedical research: in vitro gametogenesis, or IVG.
The goal of IVG is to make unlimited supplies of what Hayashi calls "artificial" eggs and sperm from any cell in the human body. That could let anyone — older, infertile, single, gay, trans — have their own genetically related babies. Besides the technical challenges that remain to be overcome, there are deep ethical concerns about how IVG might eventually be used. ... IPS cells can be made from any cell in the body and then theoretically can morph into any other kind of cell. This versatility could one day help scientists solve a long list of medical problems.
Hayashi was the first to figure out how to use iPS cells to make one of the first big breakthroughs in IVG: He turned skin cells from the tails of mice into iPS cells that he then turned into mouse eggs. ...
... Researchers at a biotech startup called Conception, based in California, claim they're about to lap the Japanese scientists. Within a year, they say they'll be ready to make human eggs they hope to try to fertilize to make human embryos. But the Americans have released few details to back up their claim.
Hayashi's skeptical.
"It's impossible," Hayashi says. "In my opinion — one year — I don't think so."
Unraveling the biology of human egg development just doesn't move that fast, he says.
That said, Hayashi thinks it's not a question if IVG will ever happen. It's more a question of when, he says, and that he and his colleagues in Japan are at least as close as the Americans to making "artificial" human embryos.
Hayashi predicts they'll have an IVG egg ready to try to fertilize within five to 10 years. ...
... In addition to waiting to publish their research before making any claims, the Japanese scientists also warn that many years of experimentation would be needed to make sure artificial IVG embryos aren't carrying dangerous genetic mutations.
"They may cause some sort of diseases, or maybe cancer, or maybe early death. So there are many possibilities," Saitou says. "Even single mutations or mistakes are really disastrous." ...
... IVG would render the biological clock irrelevant, by enabling women of any age to have genetically related children. That raises questions about whether there should be age limits for IVG baby-making.
IVG could also enable gay and trans couples to have babies genetically related to both partners, for the first time allowing families, regardless of gender identity, to have biologically related children.
Beyond that, IVG could potentially make traditional baby-making antiquated for everyone. An unlimited supply of genetically matched artificial human eggs, sperm and embryos for anyone, anytime could make scanning the genes of IVG embryos the norm.
Prospective parents would be able to minimize the chances their children would be born with detrimental genes. IVG could also lead to "designer babies," whose parents pick and choose the traits they desire.
"That [would] mean maybe exploitation of embryos, commercialization of reproduction. And also you could manipulate genetic information of those sperm and egg," says Misao Fujita, a bioethicist at the University of Kyoto who's been studying Japanese public opinion about IVG.
The Japanese public is uncomfortable with IVG for those reasons. But the Japanese would even be uneasy about using this technology to create babies outside of traditional family structures, she says.
"If you can create artificial embryos, then that mean[s] maybe a single person can create their own baby. So who is [the] mother and father? So that means social confusion," Fujita says.
... Hayashi, a developmental geneticist at Osaka University in Japan, is a pioneer in one of the most exciting — and controversial — fields of biomedical research: in vitro gametogenesis, or IVG.
The goal of IVG is to make unlimited supplies of what Hayashi calls "artificial" eggs and sperm from any cell in the human body. That could let anyone — older, infertile, single, gay, trans — have their own genetically related babies. Besides the technical challenges that remain to be overcome, there are deep ethical concerns about how IVG might eventually be used. ... IPS cells can be made from any cell in the body and then theoretically can morph into any other kind of cell. This versatility could one day help scientists solve a long list of medical problems.
Hayashi was the first to figure out how to use iPS cells to make one of the first big breakthroughs in IVG: He turned skin cells from the tails of mice into iPS cells that he then turned into mouse eggs. ...
... Researchers at a biotech startup called Conception, based in California, claim they're about to lap the Japanese scientists. Within a year, they say they'll be ready to make human eggs they hope to try to fertilize to make human embryos. But the Americans have released few details to back up their claim.
Hayashi's skeptical.
"It's impossible," Hayashi says. "In my opinion — one year — I don't think so."
Unraveling the biology of human egg development just doesn't move that fast, he says.
That said, Hayashi thinks it's not a question if IVG will ever happen. It's more a question of when, he says, and that he and his colleagues in Japan are at least as close as the Americans to making "artificial" human embryos.
Hayashi predicts they'll have an IVG egg ready to try to fertilize within five to 10 years. ...
... In addition to waiting to publish their research before making any claims, the Japanese scientists also warn that many years of experimentation would be needed to make sure artificial IVG embryos aren't carrying dangerous genetic mutations.
"They may cause some sort of diseases, or maybe cancer, or maybe early death. So there are many possibilities," Saitou says. "Even single mutations or mistakes are really disastrous." ...
... IVG would render the biological clock irrelevant, by enabling women of any age to have genetically related children. That raises questions about whether there should be age limits for IVG baby-making.
IVG could also enable gay and trans couples to have babies genetically related to both partners, for the first time allowing families, regardless of gender identity, to have biologically related children.
Beyond that, IVG could potentially make traditional baby-making antiquated for everyone. An unlimited supply of genetically matched artificial human eggs, sperm and embryos for anyone, anytime could make scanning the genes of IVG embryos the norm.
Prospective parents would be able to minimize the chances their children would be born with detrimental genes. IVG could also lead to "designer babies," whose parents pick and choose the traits they desire.
"That [would] mean maybe exploitation of embryos, commercialization of reproduction. And also you could manipulate genetic information of those sperm and egg," says Misao Fujita, a bioethicist at the University of Kyoto who's been studying Japanese public opinion about IVG.
The Japanese public is uncomfortable with IVG for those reasons. But the Japanese would even be uneasy about using this technology to create babies outside of traditional family structures, she says.
"If you can create artificial embryos, then that mean[s] maybe a single person can create their own baby. So who is [the] mother and father? So that means social confusion," Fujita says.
ChatGPT can now see, hear, and speak
We are beginning to roll out new voice and image capabilities in ChatGPT. They offer a new, more intuitive type of interface by allowing you to have a voice conversation or show ChatGPT what you’re talking about.
Voice and image give you more ways to use ChatGPT in your life. Snap a picture of a landmark while traveling and have a live conversation about what’s interesting about it. When you’re home, snap pictures of your fridge and pantry to figure out what’s for dinner (and ask follow up questions for a step by step recipe). After dinner, help your child with a math problem by taking a photo, circling the problem set, and having it share hints with both of you.
ChatGPT’s voice capability is “powered by a new text-to-speech model, capable of generating human-like audio from just text and a few seconds of sample speech,” Open AI said in the blogpost. The company added that it collaborated with professional voice actors to create the five different voices that can be used to animate the chatbot. ... The new features roll out in the app within the next two weeks for paying subscribers of ChatGPT’s Plus and Enterprise services. (Subscriptions to the Plus service are $20 a month, and its Enterprise service is currently only offered to business clients).
We are beginning to roll out new voice and image capabilities in ChatGPT. They offer a new, more intuitive type of interface by allowing you to have a voice conversation or show ChatGPT what you’re talking about.
Voice and image give you more ways to use ChatGPT in your life. Snap a picture of a landmark while traveling and have a live conversation about what’s interesting about it. When you’re home, snap pictures of your fridge and pantry to figure out what’s for dinner (and ask follow up questions for a step by step recipe). After dinner, help your child with a math problem by taking a photo, circling the problem set, and having it share hints with both of you.
ChatGPT’s voice capability is “powered by a new text-to-speech model, capable of generating human-like audio from just text and a few seconds of sample speech,” Open AI said in the blogpost. The company added that it collaborated with professional voice actors to create the five different voices that can be used to animate the chatbot. ... The new features roll out in the app within the next two weeks for paying subscribers of ChatGPT’s Plus and Enterprise services. (Subscriptions to the Plus service are $20 a month, and its Enterprise service is currently only offered to business clients).
100x Efficiency: MIT’s Machine-Learning System Based on Light Could Yield More Powerful Large Language Models
MIT system demonstrates greater than 100-fold improvement in energy efficiency and a 25-fold improvement in compute density compared with current systems.
ChatGPT has made headlines around the world with its ability to write essays, email, and computer code based on a few prompts from a user. Now an MIT-led team reports a system that could lead to machine-learning programs several orders of magnitude more powerful than the one behind ChatGPT. The system they developed could also use several orders of magnitude less energy than the state-of-the-art supercomputers behind the machine-learning models of today.
https://scitechdaily.com/100x-effici...nguage-models/
MIT system demonstrates greater than 100-fold improvement in energy efficiency and a 25-fold improvement in compute density compared with current systems.
ChatGPT has made headlines around the world with its ability to write essays, email, and computer code based on a few prompts from a user. Now an MIT-led team reports a system that could lead to machine-learning programs several orders of magnitude more powerful than the one behind ChatGPT. The system they developed could also use several orders of magnitude less energy than the state-of-the-art supercomputers behind the machine-learning models of today.
https://scitechdaily.com/100x-effici...nguage-models/
Radiologists vs. Robots: Outperforming AI in Identifying Lung Diseases on Chest X-Rays
Radiologists surpassed AI in accurately detecting three common lung diseases from chest X-rays, as per a study in the Radiology journal. AI tools, while sensitive, produced more false positives, making them less reliable for autonomous diagnoses but useful for second opinions.
https://scitechdaily.com/radiologist...-chest-x-rays/
Radiologists surpassed AI in accurately detecting three common lung diseases from chest X-rays, as per a study in the Radiology journal. AI tools, while sensitive, produced more false positives, making them less reliable for autonomous diagnoses but useful for second opinions.
https://scitechdaily.com/radiologist...-chest-x-rays/
Revolutionary AI Set To Predict Your Future Health With a Single Click
Researchers from Edith Cowan University developed software that rapidly analyzes bone density scans to detect abdominal aortic calcification (AAC), a predictor of cardiovascular events and other health risks. The software processed images with 80% agreement with experts and could revolutionize early disease detection during routine clinical practice.
https://scitechdaily.com/revolutiona...-single-click/
Researchers from Edith Cowan University developed software that rapidly analyzes bone density scans to detect abdominal aortic calcification (AAC), a predictor of cardiovascular events and other health risks. The software processed images with 80% agreement with experts and could revolutionize early disease detection during routine clinical practice.
https://scitechdaily.com/revolutiona...-single-click/
Paralyzed man regains some [Hand] function after world-first surgery
A 46-year-old Swiss man who was paralyzed after a devastating fall has regained some movement following groundbreaking surgery that appeared to successfully install an implant on his brain using artificial intelligence.
Paralyzed Man Can Use Feel Again Thanks to Groundbreaking AI
A 46-year-old Swiss man who was paralyzed after a devastating fall has regained some movement following groundbreaking surgery that appeared to successfully install an implant on his brain using artificial intelligence.
Paralyzed Man Can Use Feel Again Thanks to Groundbreaking AI
GlowTrack: Unleashing the Power of AI To Track Human and Animal Behavior
Current cutting-edge methods utilize artificial intelligence to automatically track parts of the body as they move. However, training these models is still time-intensive and limited by the need for researchers to manually mark each body part hundreds to thousands of times.
Now, Associate Professor Eiman Azim and team have created GlowTrack, a non-invasive movement-tracking method that uses fluorescent dye markers to train artificial intelligence. GlowTrack is robust, time-efficient, and high definition—capable of tracking a single digit on a mouse’s paw or hundreds of landmarks on a human hand.
https://scitechdaily.com/glowtrack-u...imal-behavior/
Current cutting-edge methods utilize artificial intelligence to automatically track parts of the body as they move. However, training these models is still time-intensive and limited by the need for researchers to manually mark each body part hundreds to thousands of times.
Now, Associate Professor Eiman Azim and team have created GlowTrack, a non-invasive movement-tracking method that uses fluorescent dye markers to train artificial intelligence. GlowTrack is robust, time-efficient, and high definition—capable of tracking a single digit on a mouse’s paw or hundreds of landmarks on a human hand.
https://scitechdaily.com/glowtrack-u...imal-behavior/
Exposing the secretive company at the forefront of facial recognition technology
Facial recognition technology is convenient when you use it to unlock your phone or log into an app. But you might be surprised to know that your face is most likely already in a facial recognition database that can be used to identify who you are without you even being aware it's happening or knowing who's using it and why.
A company expanding the technological possibilities of this technology and testing its legal and ethical limits is Clearview AI. It's a startup whose clients already include some law enforcement and government agencies. If you haven't already heard of it, it's in part because the company didn't want you to know it existed. It did its best to remain secretive until it was exposed by my guest, Kashmir Hill. She's a New York Times tech reporter who first wrote about Clearview AI in 2020. She describes her beat as the future tech dystopia and how we can try to avoid it. Kashmir has continued to report on Clearview AI and other developments in facial recognition technology. Now, she has a new book called "Your Face Belongs To Us: A Secretive Startup's Quest To End Privacy As We Know It."
... For police use of this technology, you know, it can be very useful for solving crimes, but, you know, it can also be wielded in a way that could be very chilling or intimidating. Say, if there are protesters against police brutality and the government is able to very easily identify them. And we have seen this already happen in other countries, not with Clearview AI's technology but with other facial recognition technology. In China, you know, this kind of technology has been used to identify protesters in Hong Kong, to identify Uyghur Muslims and for more surprising uses like naming and shaming people who wear pajamas in public or making sure that somebody in a public restroom doesn't take too much toilet paper. They have to look at a face recognition camera, only get a little bit of toilet paper and then wait a certain amount of time until their face can unlock more. ...
JUNDO: A fascinating interview, highly recommended:
Facial recognition technology is convenient when you use it to unlock your phone or log into an app. But you might be surprised to know that your face is most likely already in a facial recognition database that can be used to identify who you are without you even being aware it's happening or knowing who's using it and why.
A company expanding the technological possibilities of this technology and testing its legal and ethical limits is Clearview AI. It's a startup whose clients already include some law enforcement and government agencies. If you haven't already heard of it, it's in part because the company didn't want you to know it existed. It did its best to remain secretive until it was exposed by my guest, Kashmir Hill. She's a New York Times tech reporter who first wrote about Clearview AI in 2020. She describes her beat as the future tech dystopia and how we can try to avoid it. Kashmir has continued to report on Clearview AI and other developments in facial recognition technology. Now, she has a new book called "Your Face Belongs To Us: A Secretive Startup's Quest To End Privacy As We Know It."
... For police use of this technology, you know, it can be very useful for solving crimes, but, you know, it can also be wielded in a way that could be very chilling or intimidating. Say, if there are protesters against police brutality and the government is able to very easily identify them. And we have seen this already happen in other countries, not with Clearview AI's technology but with other facial recognition technology. In China, you know, this kind of technology has been used to identify protesters in Hong Kong, to identify Uyghur Muslims and for more surprising uses like naming and shaming people who wear pajamas in public or making sure that somebody in a public restroom doesn't take too much toilet paper. They have to look at a face recognition camera, only get a little bit of toilet paper and then wait a certain amount of time until their face can unlock more. ...
JUNDO: A fascinating interview, highly recommended:

Japan labor market set for change as huge worker shortage looms
Japan's labor market may be at an inflection point as the nation braces for a shortfall of millions of workers, the rise of generative AI and risks to economic security. ... In the short term, labor shortages are evident in the pandemic-hit services sector, with labor-intensive areas like nursing care and construction already struggling. ... The institute estimates 9.7 million jobs will be lost by 2035 due to the effects of digitalization, including AI. But labor will still be in short supply that year as a result of a push for green and digital transformations and efforts to boost the nation's semiconductor industry. ... One challenge for the broader Japanese labor market is that the percentage of workers with non-routine, or "creative," tasks in relation to routine ones is lower than in countries like the United States and Britain, the institute said, expecting a severe labor shortage for professional technical occupations. ...
The International Labor Organization says generative AI, which is neither inherently good nor bad, will "augment" rather than destroy jobs. The U.N. agency is calling for governments and others to design the right policies to ensure a smooth transition because costs to affected workers will be "brutal." ...
https://mainichi.jp/english/articles...0m/0bu/037000c
Japan's labor market may be at an inflection point as the nation braces for a shortfall of millions of workers, the rise of generative AI and risks to economic security. ... In the short term, labor shortages are evident in the pandemic-hit services sector, with labor-intensive areas like nursing care and construction already struggling. ... The institute estimates 9.7 million jobs will be lost by 2035 due to the effects of digitalization, including AI. But labor will still be in short supply that year as a result of a push for green and digital transformations and efforts to boost the nation's semiconductor industry. ... One challenge for the broader Japanese labor market is that the percentage of workers with non-routine, or "creative," tasks in relation to routine ones is lower than in countries like the United States and Britain, the institute said, expecting a severe labor shortage for professional technical occupations. ...
The International Labor Organization says generative AI, which is neither inherently good nor bad, will "augment" rather than destroy jobs. The U.N. agency is calling for governments and others to design the right policies to ensure a smooth transition because costs to affected workers will be "brutal." ...
https://mainichi.jp/english/articles...0m/0bu/037000c
FCC [in USA] to reintroduce rules protecting net neutrality
he US government aims to restore sweeping regulations for high-speed internet providers such as AT&T, Comcast and Verizon, reviving “net neutrality” rules for the broadband industry — and an ongoing debate about the internet’s future.
The proposed rules from the Federal Communications Commission will designate internet service — both the wired kind found in homes and businesses as well as mobile data on cellphones — as “essential telecommunications” akin to traditional telephone services, said FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel. The rules would ban internet service providers (ISPs) from blocking or slowing down access to websites and online content.
In addition to the prohibitions on blocking and throttling internet traffic, the draft rules also seek to prevent ISPs from selectively speeding up service to favored websites or to those that agree to pay extra fees, Rosenworcel said, a move designed to prevent the emergence of “fast lanes” on the web that could give some websites a paid advantage over others.
https://us.cnn.com/2023/09/26/tech/f...ers/index.html
he US government aims to restore sweeping regulations for high-speed internet providers such as AT&T, Comcast and Verizon, reviving “net neutrality” rules for the broadband industry — and an ongoing debate about the internet’s future.
The proposed rules from the Federal Communications Commission will designate internet service — both the wired kind found in homes and businesses as well as mobile data on cellphones — as “essential telecommunications” akin to traditional telephone services, said FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel. The rules would ban internet service providers (ISPs) from blocking or slowing down access to websites and online content.
In addition to the prohibitions on blocking and throttling internet traffic, the draft rules also seek to prevent ISPs from selectively speeding up service to favored websites or to those that agree to pay extra fees, Rosenworcel said, a move designed to prevent the emergence of “fast lanes” on the web that could give some websites a paid advantage over others.
https://us.cnn.com/2023/09/26/tech/f...ers/index.html
Birthplace of atomic bomb braces for biggest mission since the Manhattan Project
The community is facing growing pains as Los Alamos National Laboratory takes part in the country’s most ambitious nuclear weapons effort since World War II
... 80 years later, as Los Alamos National Laboratory takes part in the nation’s most ambitious nuclear weapons effort since World War II. The mission calls for modernizing the arsenal with droves of new workers producing plutonium cores — key components for nuclear weapons. ...
https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news...ect-rcna117097
The community is facing growing pains as Los Alamos National Laboratory takes part in the country’s most ambitious nuclear weapons effort since World War II
... 80 years later, as Los Alamos National Laboratory takes part in the nation’s most ambitious nuclear weapons effort since World War II. The mission calls for modernizing the arsenal with droves of new workers producing plutonium cores — key components for nuclear weapons. ...
https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news...ect-rcna117097
stlah





 ), but sound advice nonetheless.
), but sound advice nonetheless.






































Comment