Something for those who like to ponder and wander in logic on Emptiness.
The Zen of Technology & Scientific Discovery! (& Robots)
Collapse
X
-
All composite things are change ... a look at the future ...

... and the far past ...New research has found that the world’s next supercontinent, Amasia, will most likely form when the Pacific Ocean closes in 200 to 300 million years.
A Curtin University-led research team used a supercomputer to simulate how a supercontinent forms. They discovered that because the Earth has been cooling for billions of years, the thickness and strength of the plates under the oceans reduce with time, making it difficult for the next supercontinent to assemble by closing the “young” oceans, such as the Atlantic or Indian oceans. The study was published recently in National Science Review
https://scitechdaily.com/behold-the-...tinent-amasia/.
... and the even farther far past ...Monstrous “Mega-Earthquake” Triggered by Impact That Killed the Dinosaurs
A 6-mile (10-kilometer) asteroid hit Earth 66 million years ago, triggering the extinction of the dinosaurs. According to new evidence, the Chicxulub impact also triggered an earthquake that was so massive it shook the planet for weeks to months after the collision. This “mega-earthquake” released an incredible amount of energy, estimated at 1023 joules, which is about 50,000 times more energy than was released in the magnitude 9.1 Sumatra earthquake in 2004.
Dinosaur-Killing Asteroid Triggered Monstrous Global Tsunami With Mile-High Waves
It also triggered a monstrous tsunami with mile-high waves that scoured the ocean floor thousands of miles from the impact site on Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula, according to a new University of Michigan-led study that was published online on October 4 in the journal AGU Advances. ...“This tsunami was strong enough to disturb and erode sediments in ocean basins halfway around the globe, leaving either a gap in the sedimentary records or a jumble of older sediments,” said lead author Molly Range. She conducted the modeling study for a master’s thesis under U-M physical oceanographer and study co-author Brian Arbic and U-M paleoceanographer and study co-author Ted Moore.
... and the farther even farther far past ...Scientists Uncover the “Chemistry Behind the Origin of Life”
Purdue University chemists have discovered a mechanism for peptide-forming reactions to occur in water — something that has baffled scientists for decades.
“This is essentially the chemistry behind the origin of life,” said Graham Cooks. He is the Henry Bohn Hass Distinguished Professor of Analytical Chemistry in Purdue’s College of Science. “This is the first demonstration that primordial molecules, simple amino acids, spontaneously form peptides, the building blocks of life, in droplets of pure water. This is a dramatic discovery.”
Scientists have theorized for decades that life on Earth began in the oceans. However, the chemistry behind this remained an enigma. Raw amino acids — something that meteorites delivered to early Earth daily — can react and latch together to form peptides. These are the building blocks of proteins and, eventually, life. Strangely, the process requires the loss of a water molecule, which seems exceedingly improbable in a wet, aqueous, or oceanic environment. For life to form, it required water. However, it also needed space away from the water. ...
https://scitechdaily.com/the-fountai...rigin-of-life/
... and the fast and far away ...Supercomputer Simulations Reveal How a Giant Impact Could Have Formed the Moon
HOMESPACE NEWS
Supercomputer Simulations Reveal How a Giant Impact Could Have Formed the Moon
TOPICS:AstrophysicsDurham UniversityMoonPopular
By DURHAM UNIVERSITY OCTOBER 6, 2022
Supercomputer Simulation Moon's Origin
Credit: Durham University
Pioneering scientists from Durham University’s Institute for Computational Cosmology used the most detailed supercomputer simulations yet to reveal an alternative explanation for the Moon’s origin, 4.5 billion years ago. It revealed that a giant impact between Earth and a Mars-sized body could immediately place a Moon-like body into orbit around Earth. ...
Gassho, JConfirming a Decades-Old Prediction: Astronomers Discover a “Cataclysmic” Pair of Stars
The stars have the shortest orbit yet, circling each other every 51 minutes, confirming a decades-old prediction. ... A cataclysmic variable occurs when the two stars draw close, over billions of years, causing the white dwarf to start accreting, or eating material away from its partner star. This process can give off enormous, variable flashes of light that, centuries ago, astronomers assumed to be a result of some unknown cataclysm. ... ZTF J1813+4251 ... system [] resides about 3,000 light years from Earth, in the Hercules constellation.
The newly discovered system, which the team has tagged ZTF J1813+4251, is a cataclysmic variable with the shortest orbit detected to date. Unlike other such systems observed in the past, the astronomers caught this cataclysmic variable as the stars eclipsed each other multiple times, allowing the team to precisely measure properties of each star.
https://scitechdaily.com/confirming-...pair-of-stars/
stlahLast edited by Jundo; 10-09-2022, 04:52 AM.ALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
Yummy! Magne-meat!
... we are meat ...A Better Way To Grow Meat in the Lab: Zapping Cells With a Magnet
The new technique simplifies the production process of cell-based meat.
The new process is a more environmentally friendly, cleaner, safer, and cost-effective way to make cell-based meat.
By zapping animal cells with a magnet, researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have discovered a revolutionary method of producing cell-based meat. By using fewer animal products, this innovative method streamlines the production of cell-based meat and makes it safer, cleaner, and more cost-effective.
The benefits of cultured meat over traditional animal agriculture include a reduced carbon footprint and a lower chance of animal disease transmission. However, the current method of producing cultured meat needs the use of other animal products, which largely defeats the purpose, or drugs to stimulate the meat’s growth.
... The harvested secretomes can also be used for regenerative medicine. The NUS team used the secreted proteins to treat unhealthy cells and found that they help to accelerate the recovery and growth of unhealthy cells. Therefore, this method can potentially help to cure injured cells and speed up a patient’s recovery.
https://scitechdaily.com/a-better-wa...with-a-magnet/
Gassho, JNew RNA Tool Can Illuminate Brain Circuits and Edit Specific Cells
Scientists at Duke University have developed an RNA-based editing tool that targets individual cells, rather than genes. It is capable of precisely targeting any type of cell and selectively adding any protein of interest. Researchers said the tool could enable modifying very specific cells and cell functions to manage disease.
Using an RNA-based probe, a team led by neurobiologist Z. Josh Huang, Ph.D. and postdoctoral researcher Yongjun Qian, Ph.D. demonstrated they can introduce into cells fluorescent tags to label specific types of brain tissue; a light-sensitive on/off switch to silence or activate neurons of their choosing; and even a self-destruct enzyme to precisely expunge some cells but not others. The work will be published today (October 5, 2022) in the journal Nature.
https://scitechdaily.com/new-rna-too...pecific-cells/
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
Cassie, a robot built by Agility Robotics, set the Guinness World Record for the fastest 100-meter run by a bipedal robot.
More on Cassie and bi-pedal robots ...
Gassho, J
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
A very interesting interview with one of the prize-winners, explaining the history of thinking about "spooky action at a distance" aka "quantum entanglement, and these experiments which confirmed it and led to this prize award ...Something for those who like to ponder and wander in logic on Emptiness.
https://www.scientificamerican.com/a...ers-proved-it/
Gassho, J
A Q&A with Caltech alumnus John Clauser on his first experimental proof of quantum entanglement.
When scientists, including Albert Einstein and Erwin Schrödinger, first discovered the phenomenon of entanglement in the 1930s, they were perplexed. Disturbingly, entanglement required two separated particles to remain connected without being in direct contact. In fact, Einstein famously called entanglement “spooky action at a distance,” because the particles seemed to be communicating faster than the speed of light.
To explain the bizarre implications of entanglement, Einstein, along with Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen (EPR), argued that “hidden variables” should be added to quantum mechanics. These could be used to explain entanglement, and to restore “locality” and “causality” to the behavior of the particles. Locality states that objects are only influenced by their immediate surroundings. Causality states that an effect cannot occur before its cause, and that causal signaling cannot propagate faster than light speed. Niels Bohr famously disputed EPR’s argument, while Schrödinger and Wendell Furry, in response to EPR, independently hypothesized that entanglement vanishes with wide-particle separation.
Unfortunately, at the time, no experimental evidence for or against quantum entanglement of widely separated particles was available. Experiments have since proven that entanglement is very real and fundamental to nature. Furthermore, quantum mechanics has now been proven to work, not only at very short distances but also at very great distances. Indeed, China’s quantum-encrypted communications satellite, Micius, (part of the Quantum Experiments at Space Scale (QUESS) research project) relies on quantum entanglement between photons that are separated by thousands of kilometers.
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
Good news, I would say personally ... since all composite things are impermanent, including us, but we don't want to rush things.
The DART mission successfully changed the motion of an asteroid
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test successfully changed the trajectory of the asteroid Dimorphos when the NASA spacecraft intentionally slammed into the space rock on September 26, according to the agency.
The DART mission, a full-scale demonstration of deflection technology, was the world’s first conducted on behalf of planetary defense. The mission was also the first time humanity intentionally changed the motion of a celestial object in space.
Prior to impact, it took Dimorphos 11 hours and 55 minutes to orbit its larger parent asteroid Didymos. Astronomers used ground-based telescopes to measure how Dimorphos’ orbit changed after impact. Now, it takes Dimorphos 11 hours and 23 minutes to circle Didymos. The DART spacecraft changed the moonlet asteroid’s orbit by 32 minutes.
Initially, astronomers expected DART to be a success if it shortened the trajectory by 10 minutes.
“All of us have a responsibility to protect our home planet. After all, it’s the only one we have,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson.https://us.cnn.com/2022/10/11/world/...scn/index.html
That second video from NASA makes it sound like we are getting our revenge!
Darn you asteroids! REMEMBER THE DINOSAURS! ...
Gassho, J
stlahLast edited by Jundo; 10-12-2022, 12:25 AM.ALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
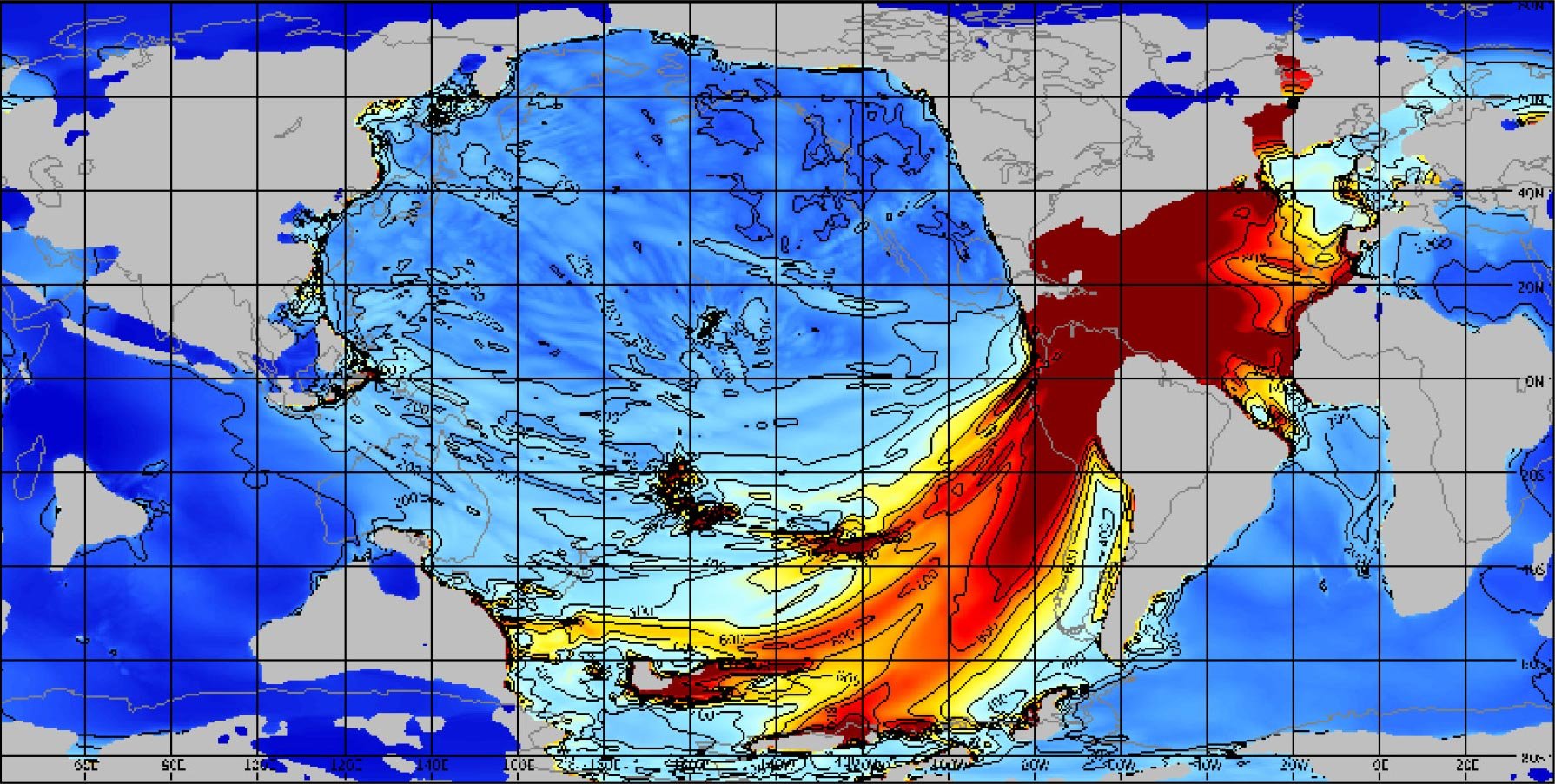
Where our Milky Way Galaxy puts its old used stars out for recycling ...
Milky Way WITHOUT showing the "Galactic Underworld" ...The Milky Way galaxy has a graveyard of dead stars that stretches three times the height of the galaxy, according to new research. Astronomers found the ancient stellar remnants when they mapped this “galactic underworld” for the first time.
Our galaxy, which formed about 13 billion years ago, has been the home of billions of stars. Over time, many of these massive objects have collapsed into dense remnants.
When a star more than eight times larger than the sun burns through its elements and collapses, the outer layers of the star explode in a supernova. Meanwhile, the stellar core condenses into either a neutron star or black hole. ... The very supernova explosions that triggered the collapse of the stars actually kicked them out into interstellar space. Researchers determined that 30% of those stellar remnants have been kicked out of the galaxy completely, according to their study published in the latest issue of the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
The research team was able to map where the stellar remains rest within and around our galaxy by recreating the life cycle of the ancient stars. “One of the problems for finding these ancient objects is that, until now, we had no idea where to look,” said study coauthor Peter Tuthill, professor at the School of Physics and director of the Sydney Institute for Astronomy at The University of Sydney in Australia, in a statement.
... “Almost all the remnants ever formed are still out there, sliding like ghosts through interstellar space,” Sweeney said.
The new map includes where the stars were born within the Milky Way, where they exploded and their eventual resting places.

Milky Way WITH the "Galactic Underworld" ...Comparing the Milky Way’s current appearance with the new model of its stellar necropolis shows striking differences. The galaxy’s characteristic spiral arms seem to disappear beneath all of the supernova kicks that wash them out.
The “galactic underworld” also appears taller and more puffy than the Milky Way because the supernova kicks pushed the remnants into a kind of halo formation around the galaxy.

Gassho, J
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
It is amazing what we can do with Photoshop ...
Science enthusiasts have processed the new JunoCam images of Jupiter’s icy moon, with results that are out of this world.
Citizen scientists have furnished unique perspectives of the recent close flyby of Jupiter’s icy moon Europa by NASA’s Juno spacecraft. By processing raw images from JunoCam, the spacecraft’s public-engagement camera, members of the general public have created deep-space portraits of the Jovian moon that are not only spectacular, but also worthy of further scientific investigation.
... Europa is the solar system’s sixth-largest moon with about 90% of the equatorial diameter of Earth’s moon. Scientists are confident a salty ocean lies below a miles-thick ice shell, sparking questions about the potential habitability of the ocean. In the early 2030s, NASA’s Europa Clipper spacecraft will arrive and strive to answer these questions about Europa’s habitability. The data from the Juno flyby provides a preview of what that mission will reveal
... The images and spectra of Europa, published in the Planetary Science Journal, reveal that Europa’s crust is mainly composed of frozen water ice with non-ice materials contaminating the surface. Oliver King from the University of Leicester School of Physics and Astronomy said: “We mapped the distributions of the different materials on the surface, including sulphuric acid frost which is mainly found on the side of Europa that is most heavily bombarded by the gases surrounding Jupiter.” “The modeling found that there could be a variety of different salts present on the surface, but suggested that infrared spectroscopy alone is generally unable to identify which specific types of salt are present.” ... With this additional data about Europa’s geology, Juno’s observations will benefit future missions to the Jovian moon, including NASA’s Europa Clipper. That mission, set to launch in 2024, will study Europa’s atmosphere, surface, and interior. Its main science goal will be to determine whether there are locations below the moon’s surface that could support life.
https://scitechdaily.com/enhance-cit...om-nasas-juno/

Gassho, J
stlahLast edited by Jundo; 10-12-2022, 12:17 AM.ALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
Using our brains ... or parts of them anyway ...
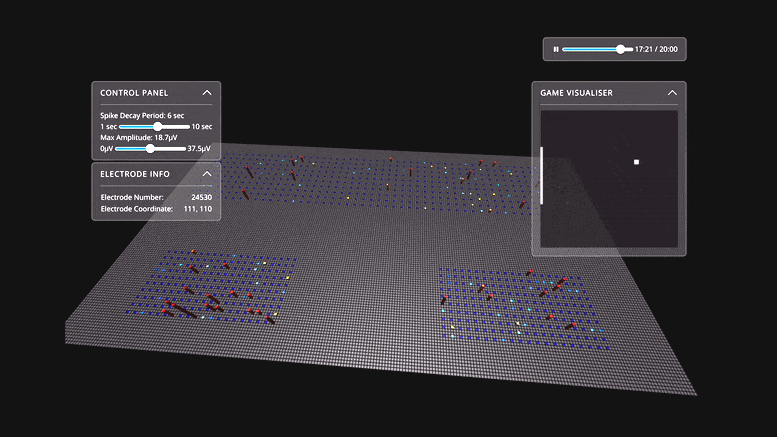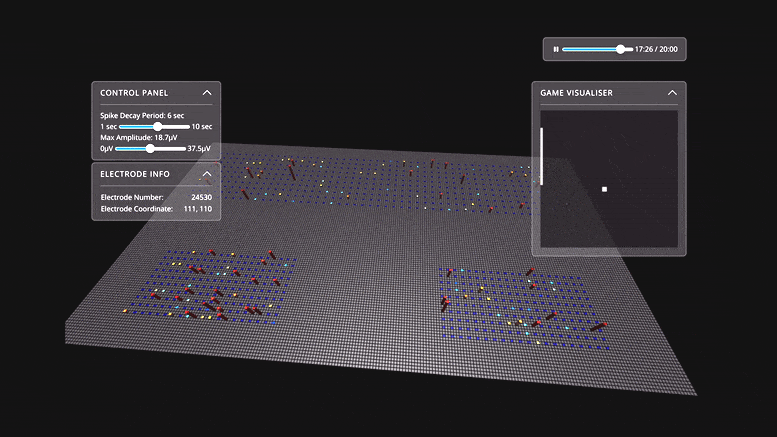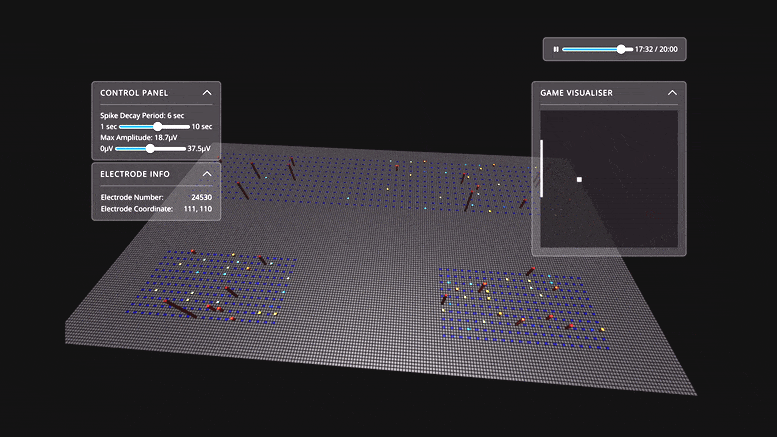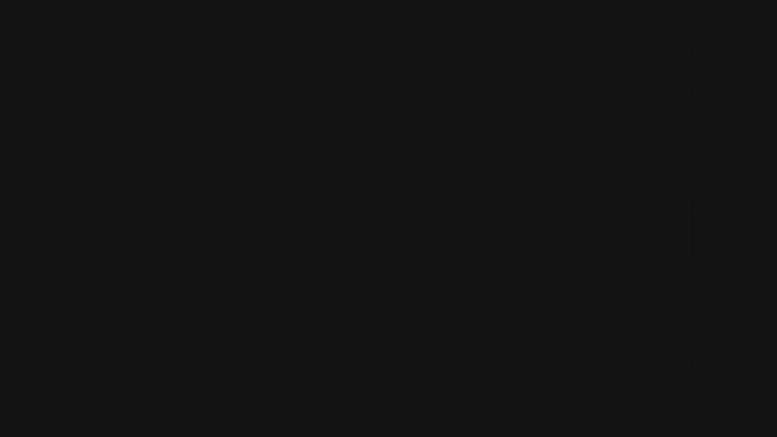
... and ... people sometimes think like rats ... and rats now think like people ...Watch Live Human Brain Cells in a Dish Learn To Play Pong
Scientists have shown for the first time that 800,000 brain cells living in a dish can perform goal-directed tasks. In this case, they played the simple tennis-like computer game, Pong. The results of the Melbourne-led study are published today (October 12) in the journal Neuron. ... “We have shown we can interact with living biological neurons in such a way that compels them to modify their activity, leading to something that resembles intelligence,” says lead author Dr. Brett Kagan. ... Although researchers have been able to mount neurons on multi-electrode arrays and read their activity for some time now, this is the first time that cells have been stimulated in a structured and meaningful way. “In the past, models of the brain have been developed according to how computer scientists think the brain might work,” Kagan says. “That is usually based on our current understanding of information technology, such as silicon computing.
“But in truth, we don’t really understand how the brain works.”
By constructing a living model brain from basic structures in this way, scientists will be able to experiment using real brain function rather than flawed analogous models such as a computer.
For example, Kagan and his team will next experiment to see what effect alcohol has when introduced to DishBrain.
“We’re trying to create a dose-response curve with ethanol – basically get them ‘drunk’ and see if they play the game more poorly, just as when people drink,” says Kagan. “This new capacity to teach cell cultures to perform a task in which they exhibit sentience – by controlling the paddle to return the ball via sensing – opens up new discovery possibilities which will have far-reaching consequences for technology, health, and society,” ...
... Electrodes on the left or right of one array were fired to tell Dishbrain which side the ball was on, while the distance from the paddle was indicated by the frequency of signals. Feedback from the electrodes taught DishBrain how to return the ball, by making the cells act as if they themselves were the paddle.
“We’ve never before been able to see how the cells act in a virtual environment,” says Kagan. “We managed to build a closed-loop environment that can read what’s happening in the cells, stimulate them with meaningful information and then change the cells in an interactive way so they can actually alter each other.”
[Below is a visual representation of the simulated Pong environment where neuron activity is reflected in the tiles growing in height.]
Gassho, JHuman ‘mini-brains’ implanted in rats prompt excitement — and concern
Miniature human brain-like structures transplanted into rats can send signals and respond to environmental cues picked up by the rats’ whiskers, according to a study1. This demonstration that neurons grown from human stem cells can interface with nerve cells in live rodents could lead to a way to test therapies for human brain disorders. ...
... neuroscientist Sergiu Pasca at Stanford University in California and his colleagues grew the structures from human stem cells and then injected them into the brains of newborn rat pups, with the expectation that the human cells would grow along with the rats’ own cells. The team placed the organoids in a brain region called the somatosensory cerebral cortex, which receives signals from the rats’ whiskers and other sensory organs and then passes them along to other brain regions that interpret the signals. Human brain cells mature much more slowly than rat cells, so the researchers had to wait for more than six months for the organoids to become fully integrated into the rat brains. But when they examined the animals’ brains at the end of that time, they saw that the integration had been so successful that it was almost like adding “another transistor to a circuit”, Pasca said at a 10 October press conference. ...
... In their report, published in Nature on 12 October1, the researchers describe how they genetically engineered the neurons in the organoids to fire when stimulated with light from a fibre-optic cable embedded in the rats’ brains. The team trained the rats to lick a spout to receive water while the light was switched on. Afterwards, when the researchers shone the light on the hybrid brains, the rats were prompted to lick the spout, meaning that the human cells had become integrated well enough to help drive the animals’ behaviour. Furthermore, when the researchers tweaked the rats’ whiskers, they found that the human cells in the sensory cortex fired in response, suggesting that the cells were able to pick up sensory information. ...
... Some of the challenges are ethical. People are concerned that creating rodent–human hybrids could harm the animals, or create animals with human-like brains. Last year, a panel organized by the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine released a report concluding that human brain organoids are still too primitive to become conscious, attain human-like intelligence or acquire other abilities that might require legal regulation. Pasca says that his team’s organoid transplants didn’t cause problems such as seizures or memory deficits in the rats, and didn’t seem to change the animals’ behaviour significantly.
But Arlotta, a member of the National Academies panel, says that problems could arise as science advances. “We can’t just discuss it once and let it be,” she says. She adds that concerns about human organoids need to be weighed against the needs of people with neurological and psychiatric disorders. Brain organoids and human–animal hybrid brains could reveal the mechanisms underlying these illnesses, and allow researchers to test therapies for conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. “I think we have a responsibility as a society to do everything we can,” Arlotta says.
[PICTURE: Researchers have transplanted a human brain organoid (bright green) into the brain of a newborn rat pup, creating hybrid brains in which the neurons interface.]
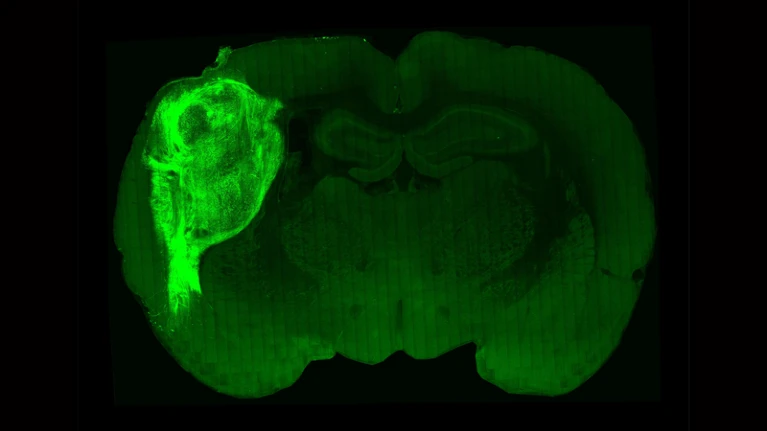 Last edited by Jundo; 10-13-2022, 01:47 AM.ALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLE
Last edited by Jundo; 10-13-2022, 01:47 AM.ALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
Our common root with mice and elephants ...
Gassho, JScientists Reconstruct the Genome of the 180-Million-Year-Old Common Ancestor of All Mammals
From a platypus to a blue whale, all living mammals today are descended from a common ancestor that existed some 180 million years ago. Although we don’t know a lot about this animal, a global team of experts has recently computationally reconstructed the organization of its genome. The findings were recently published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Our results have important implications for understanding the evolution of mammals and for conservation efforts,” said Harris Lewin, distinguished professor of evolution and ecology at the University of California, Davis, and senior author on the paper. ... The researchers identified 1,215 blocks of genes that appear on the same chromosome in the same order across all 32 genomes. Damas said that these building blocks of all mammal genomes include genes that are essential for the development of a normal embryo. ... “This remarkable finding shows the evolutionary stability of the order and orientation of genes on chromosomes over an extended evolutionary timeframe of more than 320 million years,” Lewin said.
In contrast, regions between these conserved blocks contained more repetitive sequences and were more prone to breakages, rearrangements, and sequence duplications, which are major drivers of genome evolution. ... The researchers were able to follow the ancestral chromosomes forward in time from the common ancestor. They found that the rate of chromosome rearrangement differed between mammal lineages. For example, in the ruminant lineage (leading to modern cattle, sheep, and deer) there was an acceleration in rearrangement 66 million years ago when an asteroid impact killed off the dinosaurs and led to the rise of mammals.
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
Our first baby steps ...
And a fascinating look at our stellar face, and its changes ...
A new study demonstrates how the pelvis evolved for upright walking.
If evolutionary biologist Terence D. Capellini were to rank the body parts that define us as human, the pelvis would be towards the top.
After all, thanks to its design, humans can walk upright on two legs (unlike our primate cousins) and mothers can give birth to children with huge heads (therefore big brains). The pelvis is anatomically well-understood, but when it comes to how and when this very essential structure takes form throughout development, our understanding begins to falter.
... The study shows that many of the features essential for human walking and birth form around the 6- to 8-week mark during pregnancy. This includes key pelvic features unique to humans, like its curved and basin-like shape. The formation happens while bones are still cartilage so they can easily, curve, rotate, expand, and grow.
The researchers also discovered that when other cartilage in the body starts to transform into bone, the developing pelvic region remains as cartilage for a longer period of time, allowing it to mature properly.
“There appears to be a stalling that happens and this stalling allows the cartilage to still grow, which was pretty interesting to find and surprising,” Capellini said. “I call it a zone of protection.”
The researchers used RNA sequencing to determine which genes in the area are actively triggering pelvic formation and slowing ossification, which usually converts softer cartilage to hard bone. They discovered hundreds of genes that are turned either on or off throughout the 6- to 8-week period to form the ilium in the pelvis, which is the largest and uppermost bone of the hip with blade-like structures that curve and rotate into a basin to support walking on two legs.
Compared to chimpanzees and gorillas, the shorter and wider reorientation of our pelvic blades makes it so humans don’t have to shift the mass of our weight forward and use our knuckles to walk or balance more comfortably. It also helps increase the size of the birth canal. Apes on the other hand have much narrower birth canals and more elongated ilium bones.
https://scitechdaily.com/why-do-huma...al-the-secret/
NASA’s NEOWISE Space Telescope Takes 12-Year Time-Lapse Movie of Entire Sky
NASA’s Near-Earth Object Wide Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or NEOWISE, spacecraft completes one trip halfway around the Sun every six months, taking images in all directions. Once stitched together, those images form an “all-sky” map showing the location and brightness of hundreds of millions of objects. Using 18 all-sky maps produced by the spacecraft (with the 19th and 20th to be released in March 2023), astronomers have constructed what is essentially a time-lapse movie of the sky, revealing changes that span a decade.
Each all-sky map is a tremendously valuable resource for astronomers by itself. However, when viewed in sequence as a time-lapse, they serve as an even more powerful tool for attempting to unlock the secrets of the universe. Comparing the maps can reveal distant objects that have changed position or brightness over time. This is known as time-domain astronomy.
https://scitechdaily.com/nasas-neowi...of-entire-sky/
Gassho, J
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
I predict that this may be a great discovery ... or that it won't be ...
Gassho, JScientists Use Machine Learning To Peer Into the Future
Chaotic physical processes are now easier to predict thanks to a new algorithm.
While the past may be a fixed and unchangeable point, machine learning can sometimes make predicting the future easier.
Researchers at The Ohio State University have recently discovered a new way to predict the behavior of spatiotemporal chaotic systems, such as changes in Earth’s weather, that are particularly difficult for scientists to forecast using a new type of machine learning technique called next generation reservoir computing.
The research, which was recently published in the journal Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, makes use of a brand-new, highly efficient algorithm that, when combined with next-generation reservoir computing, can learn spatiotemporal chaotic systems in a fraction of the time required by traditional machine learning algorithms.
Researchers put their method to the test by predicting the behavior of an atmospheric weather model, a challenging problem that has been researched extensively in the past. The Ohio State team’s algorithm is more accurate and needs 400 to 1,250 times less training data to generate better predictions than its rival, traditional machine learning algorithms that can do the same tasks. They used a laptop running Windows 10 to make predictions in a fraction of a second, which is roughly 240,000 times faster than conventional machine learning algorithms. Their method is also less computationally expensive; whereas solving complex computing problems previously required a supercomputer.
“This is very exciting, as we believe it’s a substantial advance in terms of data processing efficiency and prediction accuracy in the field of machine learning,” said Wendson De Sa Barbosa, lead author and a postdoctoral researcher in physics at Ohio State. He said that learning to predict these extremely chaotic systems is a “physics grand challenge,” and understanding them could pave the way to new scientific discoveries and breakthroughs.
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
A bit beyond my brain to fathom, quantum or otherwise, but fascinating nonetheless ...
Shocking Experiment Indicates Our Brains Use Quantum Computation
Scientists believe our brains could use quantum computation after taking a concept developed to prove the existence of quantum gravity and adapting it to explore the human brain and its workings. The discovery may shed light on consciousness, the workings of which remain scientifically difficult to understand and explain. Quantum brain processes could also explain why humans can still outperform supercomputers when it comes to unforeseen circumstances, decision-making, or learning something new.
After adapting an idea developed to prove the existence of quantum gravity to explore the human brain and its workings, researchers from Trinity College Dublin think that human brains could use quantum computation. The brain functions measured in the experiment were also correlated to short-term memory performance and conscious awareness. This suggests that quantum processes are also part of cognitive and conscious brain functions.
If the team’s results can be corroborated, which would likely require advanced multidisciplinary approaches, they would improve our general understanding of how the brain works. The insights could potentially reveal how the brain can be maintained or even healed. They may also help uncover innovative technologies and build even more advanced quantum computers.
Dr. Christian Kerskens is the co-author of the research article that was published on October 7 in the Journal of Physics Communications. He is also lead physicist at the Trinity College Institute of Neuroscience (TCIN), He said:
“We adapted an idea, developed for experiments to prove the existence of quantum gravity, whereby you take known quantum systems, which interact with an unknown system. If the known systems entangle, then the unknown must be a quantum system, too. It circumvents the difficulties to find measuring devices for something we know nothing about.
“For our experiments, we used proton spins of ‘brain water’ as the known system. ‘Brain water’ builds up naturally as fluid in our brains and the proton spins can be measured using MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging). Then, by using a specific MRI design to seek entangled spins, we found MRI signals that resemble heartbeat-evoked potentials, a form of EEG signals. EEGs measure electrical brain currents, which some people may recognize from personal experience or simply from watching hospital dramas on TV.”
Electrophysiological potentials like the heartbeat-evoked potentials are normally not detectable with MRI and the scientists believe they could only observe them because the nuclear proton spins in the brain were entangled.
“If entanglement is the only possible explanation here then that would mean that brain processes must have interacted with the nuclear spins, mediating the entanglement between the nuclear spins. As a result, we can deduce that those brain functions must be quantum.
“Because these brain functions were also correlated to short-term memory performance and conscious awareness, it is likely that those quantum processes are an important part of our cognitive and conscious brain functions.
“Quantum brain processes could explain why we can still outperform supercomputers when it comes to unforeseen circumstances, decision making, or learning something new. Our experiments performed only 50 meters away from the lecture theater, where Schrödinger presented his famous thoughts about life, may shed light on the mysteries of biology, and on consciousness which scientifically is even harder to grasp.”

Gassho, J
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
Scientists used their big brains to find this ...
Gassho, JScientists Uncover the Gene Responsible for Human’s Big Brain
Great ape animal studies have long been prohibited in Europe due to ethical concerns. An alternative to using animals in studies is the use of so-called organoids, which are three-dimensional cell structures that can be generated in the lab and are just a few millimeters in size. These organoids can be created using pluripotent stem cells, which then subsequently develop into particular cell types like nerve cells. The study team was able to create both chimpanzee and human brain organoids by using this method.
“These brain organoids allowed us to investigate a central question concerning ARHGAP11B,” says Wieland Huttner of the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, one of the three lead authors of the study.
“In a previous study, we were able to show that ARHGAP11B can enlarge a primate brain. However, it was previously unclear whether ARHGAP11B had a major or minor role in the evolutionary enlargement of the human neocortex,” says Wieland Huttner. ... “Our study shows that the gene in chimpanzee organoids causes an increase in relevant brain stem cells and an increase in those neurons that play a crucial role in the extraordinary mental abilities of humans,” said Michael Heide, the study’s lead author, who is head of the Junior Research Group Brain Development and Evolution at the German Primate Center and employee at the MPI-CBG.
When the ARGHAP11B gene was knocked out in human brain organoids or the ARHGAP11B protein’s function was inhibited, the number of these brain stem cells was reduced to that of a chimpanzee.
https://scitechdaily.com/scientists-...ans-big-brain/
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment
-
But wait a second ...
So, does that mean that, if we were to crispr ARGHAP11B into a chimpanzee brain, the result is this?When the ARGHAP11B gene was knocked out in human brain organoids or the ARHGAP11B protein’s function was inhibited, the number of these brain stem cells was reduced to that of a chimpanzee.
Fiction becomes fact?
Gassho, J
stlahALL OF LIFE IS OUR TEMPLEComment


Comment