When Australia becomes the top ...
Map of the heavens ...
BIGthink ...
Not just giant hurricanes this week ...
From Covid to the Moon ...
Mars was once lovely ...
Are we alone ...
Be conscious of this ...
Time is a state of mind ...
Swarm ...
Better that than this ...
Better this ...
One reason workers are upset ...
Clone wars ....
Also not good ...
And I thought that I was old!
Diversity ...
Saving energy ...
Two brains and two butts ...
Gassho, J
stlah
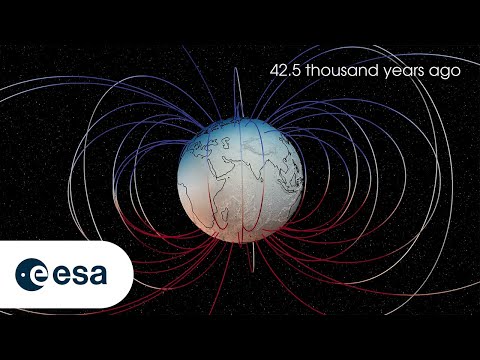
The Creepy Sounds the Earth Made When Its Magnetic Field Flipped Will Haunt Your Dreams
Using data from the European Space Agency's three-satellite Swarm mission delving deep into our planet's magnetic field, Danish and German researchers have managed to map and recreate the sounds of what is known as the Laschamp event, which resulted in Earth's magnetic field briefly flipping 41,000 years ago.
During this event, which was named after the Laschamps lava flows in France where evidence of this flip was first discovered in the 1960s, our planet's magnetic field weakened to just five percent of its normal strength.
This allowed a bunch of cosmic rays to get past the atmosphere — and as researchers from the Technical University of Denmark and the German Research Center for Geosciences show in their recreation, it made a terrible sound as well. LINK
Using data from the European Space Agency's three-satellite Swarm mission delving deep into our planet's magnetic field, Danish and German researchers have managed to map and recreate the sounds of what is known as the Laschamp event, which resulted in Earth's magnetic field briefly flipping 41,000 years ago.
During this event, which was named after the Laschamps lava flows in France where evidence of this flip was first discovered in the 1960s, our planet's magnetic field weakened to just five percent of its normal strength.
This allowed a bunch of cosmic rays to get past the atmosphere — and as researchers from the Technical University of Denmark and the German Research Center for Geosciences show in their recreation, it made a terrible sound as well. LINK
1.5 Billion Objects: Astronomers Unveil Unprecedented Infrared Map of Our Milky Way
In a monumental achievement, astronomers using the European Southern Observatory’s VISTA telescope have created the most comprehensive infrared map of the Milky Way, featuring over 1.5 billion cosmic objects. This map, derived from 500 terabytes of data collected over 13 years, reveals hidden stars, moving celestial bodies, and distant clusters, transforming our understanding of the galaxy. ... “We made so many discoveries, we have changed the view of our galaxy forever” ...
... This collage highlights a small selection of regions of the Milky Way imaged as part of the most detailed infrared map ever of our galaxy. Here we see, from left to right and top to bottom: NGC 3576, NGC 6357, Messier 17, NGC 6188, Messier 22, and NGC 3603. All of them are clouds of gas and dust where stars are forming, except Messier 22, which is a very dense group of old stars ...
.
LINK
In a monumental achievement, astronomers using the European Southern Observatory’s VISTA telescope have created the most comprehensive infrared map of the Milky Way, featuring over 1.5 billion cosmic objects. This map, derived from 500 terabytes of data collected over 13 years, reveals hidden stars, moving celestial bodies, and distant clusters, transforming our understanding of the galaxy. ... “We made so many discoveries, we have changed the view of our galaxy forever” ...
... This collage highlights a small selection of regions of the Milky Way imaged as part of the most detailed infrared map ever of our galaxy. Here we see, from left to right and top to bottom: NGC 3576, NGC 6357, Messier 17, NGC 6188, Messier 22, and NGC 3603. All of them are clouds of gas and dust where stars are forming, except Messier 22, which is a very dense group of old stars ...
.
LINK
Rewriting Cosmic Calculations: New AI Unlocks the Universe’s Settings
Using artificial intelligence, researchers have advanced the precision in estimating critical cosmological parameters by analyzing galaxy distributions. This new method, SimBIG, could provide clearer insights into the universe’s structure and help address the Hubble tension by refining our understanding of dark matter, dark energy, and the universe’s expansion. ... Compared to conventional techniques using the same galaxy data, the approach yielded less than half the uncertainty for the parameter describing the clumpiness of the universe’s matter. Additionally, the AI-powered method closely agreed with estimates of the cosmological parameters based on observations of other phenomena, such as the universe’s oldest light. ... LINK
Using artificial intelligence, researchers have advanced the precision in estimating critical cosmological parameters by analyzing galaxy distributions. This new method, SimBIG, could provide clearer insights into the universe’s structure and help address the Hubble tension by refining our understanding of dark matter, dark energy, and the universe’s expansion. ... Compared to conventional techniques using the same galaxy data, the approach yielded less than half the uncertainty for the parameter describing the clumpiness of the universe’s matter. Additionally, the AI-powered method closely agreed with estimates of the cosmological parameters based on observations of other phenomena, such as the universe’s oldest light. ... LINK
Sun Unleashes Monumental X9.0 Solar Flare – Most Intense in 7 Years – Captured by NASA Observatory
On October 3, 2024, the Sun emitted an exceptionally powerful X9.0 solar flare, peaking at 8:18 a.m. ET. This event, captured vividly by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, now stands as the most intense solar flare of Solar Cycle 25, which commenced in December 2019, eclipsing the previous high of X8.7 in May 2024.
In fact, it’s the most formidable flare observed in the last seven years, since the X11.9 flare on September 10, 2017.... The arrival of the energetic particles from a solar flare can take from 15 minutes to several hours or days, depending on the flare’s intensity and the speed of the ejection. High-energy particles can degrade the performance and lifespan of satellites and other spacecraft. They can also pose risks to astronauts, particularly those outside the protection of Earth’s magnetic field. On the ground, intense flares can disrupt telecommunications and navigation systems and, in extreme cases, cause electric power outages.
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this imagery of an X9.0 solar flare – as seen in the bright flash in the center – on October 3, 2024.
LINK
On October 3, 2024, the Sun emitted an exceptionally powerful X9.0 solar flare, peaking at 8:18 a.m. ET. This event, captured vividly by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, now stands as the most intense solar flare of Solar Cycle 25, which commenced in December 2019, eclipsing the previous high of X8.7 in May 2024.
In fact, it’s the most formidable flare observed in the last seven years, since the X11.9 flare on September 10, 2017.... The arrival of the energetic particles from a solar flare can take from 15 minutes to several hours or days, depending on the flare’s intensity and the speed of the ejection. High-energy particles can degrade the performance and lifespan of satellites and other spacecraft. They can also pose risks to astronauts, particularly those outside the protection of Earth’s magnetic field. On the ground, intense flares can disrupt telecommunications and navigation systems and, in extreme cases, cause electric power outages.
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this imagery of an X9.0 solar flare – as seen in the bright flash in the center – on October 3, 2024.
LINK
COVID-19 Pandemic Affected the Moon, Scientists Claim
As detailed in a recent article published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters, scientists from the Physical Research Laboratory in Ahmedabad, India, observed that lunar nighttime surface temperatures dipped substantially across six observation sites on the near side of the Moon. ... They propose that this "anomalous dip" was caused by a sudden drop in radiation being emitted from Earth as human activity plummeted during global lockdowns, which limited the amount of pollution and overall heat released by our planet at night. ... LINK
As detailed in a recent article published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters, scientists from the Physical Research Laboratory in Ahmedabad, India, observed that lunar nighttime surface temperatures dipped substantially across six observation sites on the near side of the Moon. ... They propose that this "anomalous dip" was caused by a sudden drop in radiation being emitted from Earth as human activity plummeted during global lockdowns, which limited the amount of pollution and overall heat released by our planet at night. ... LINK
NASA’s Curiosity Rover Uncovers the Red Planet’s Shocking Climate Shift
This is an artist’s concept of an early Mars with liquid water (blue areas) on its surface. Ancient regions on Mars bear signs of abundant water – such as features resembling valleys and deltas, and minerals that only form in the presence of liquid water. Scientists think that billions of years ago, the atmosphere of Mars was much denser and warm enough to form rivers, lakes, and perhaps even oceans of water. As the planet cooled and lost its global magnetic field, the solar wind and solar storms eroded away to space a significant amount of the planet’s atmosphere, turning Mars into the cold, arid desert we see today. LINK
.
This is an artist’s concept of an early Mars with liquid water (blue areas) on its surface. Ancient regions on Mars bear signs of abundant water – such as features resembling valleys and deltas, and minerals that only form in the presence of liquid water. Scientists think that billions of years ago, the atmosphere of Mars was much denser and warm enough to form rivers, lakes, and perhaps even oceans of water. As the planet cooled and lost its global magnetic field, the solar wind and solar storms eroded away to space a significant amount of the planet’s atmosphere, turning Mars into the cold, arid desert we see today. LINK
.
Paper Proposes New Way to Calculate Number of Alien Civilizations
Speaking to Universe Today, Columbia astronomer and paper coauthor David Kipping suggested that so-called "SETI optimists" may be missing the forest for the trees as they seek answers within our Milky Way. ... When doing calculations along this "birth-death" version of the Drake equation, the possibility arises that humanity simply happened to come about during a time when other extraterrestrial civilizations in our galaxy are rare or nonexistent. Even if that's true, though, there could be plenty more beyond it.
"I think my favorite way out is that our galaxy is just unusually quiet, most are busy and filled, but we are the first in the Milky Way," Kipping concluded. "This seems improbable, but perhaps being born in a busy galaxy is impossible since the habitable real estate has already been gobbled up. This suggests we should put more emphasis on extra-galactic SETI as our best shot." LINK
Speaking to Universe Today, Columbia astronomer and paper coauthor David Kipping suggested that so-called "SETI optimists" may be missing the forest for the trees as they seek answers within our Milky Way. ... When doing calculations along this "birth-death" version of the Drake equation, the possibility arises that humanity simply happened to come about during a time when other extraterrestrial civilizations in our galaxy are rare or nonexistent. Even if that's true, though, there could be plenty more beyond it.
"I think my favorite way out is that our galaxy is just unusually quiet, most are busy and filled, but we are the first in the Milky Way," Kipping concluded. "This seems improbable, but perhaps being born in a busy galaxy is impossible since the habitable real estate has already been gobbled up. This suggests we should put more emphasis on extra-galactic SETI as our best shot." LINK
MIT Scientists Shed New Light on the Critical Brain Connections That Define Consciousness
A new study provides further evidence that consciousness depends on communication between the brain’s sensory and cognitive regions in the cortex.
Our brains are constantly making predictions about our surroundings, enabling us to focus on and respond to unexpected events. A recent study explores how this predictive process functions during consciousness and how it changes under general anesthesia. The findings support the idea that conscious thought relies on synchronized communication between basic sensory areas and higher-order cognitive regions of the brain, facilitated by brain rhythms in specific frequency bands. ....
The new results published Oct. 7 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show that when animals were under propofol-induced general anesthesia, a sensory region retained the capacity to detect simple surprises but communication with a higher cognitive region toward the front of the brain was lost, making that region unable to engage in its “top-down” regulation of the activity of the sensory region and keeping it oblivious to simple and more complex surprises alike.
“What we are doing here speaks to the nature of consciousness,” said co-senior author Earl K. Miller, Picower Professor in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and MIT’s Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences. “Propofol general anesthesia deactivates the top-down processes that underlie cognition. It essentially disconnects communication between the front and back halves of the brain.” LINK
A new study provides further evidence that consciousness depends on communication between the brain’s sensory and cognitive regions in the cortex.
Our brains are constantly making predictions about our surroundings, enabling us to focus on and respond to unexpected events. A recent study explores how this predictive process functions during consciousness and how it changes under general anesthesia. The findings support the idea that conscious thought relies on synchronized communication between basic sensory areas and higher-order cognitive regions of the brain, facilitated by brain rhythms in specific frequency bands. ....
The new results published Oct. 7 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show that when animals were under propofol-induced general anesthesia, a sensory region retained the capacity to detect simple surprises but communication with a higher cognitive region toward the front of the brain was lost, making that region unable to engage in its “top-down” regulation of the activity of the sensory region and keeping it oblivious to simple and more complex surprises alike.
“What we are doing here speaks to the nature of consciousness,” said co-senior author Earl K. Miller, Picower Professor in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and MIT’s Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences. “Propofol general anesthesia deactivates the top-down processes that underlie cognition. It essentially disconnects communication between the front and back halves of the brain.” LINK
UCLA Scientists Reveal How Brain Cells Encode the Flow of Time
A groundbreaking study conducted by UCLA Health has begun to unravel one of the fundamental mysteries in neuroscience – how the human brain encodes and makes sense of the flow of time and experiences.
The study, published in the journal Nature, directly recorded the activity of individual neurons in humans and found specific types of brain cells fired in a way that mostly mirrored the order and structure of a person’s experience. They found the brain retains these unique firing patterns after the experience is concluded and can rapidly replay them while at rest.
Furthermore, the brain is also able to utilize these learned patterns to ready itself for future stimuli following that experience. These findings provide the first empirical evidence regarding how specific brain cells integrate “what” and “when” information to extract and retain representations of experiences through time. LINK
A groundbreaking study conducted by UCLA Health has begun to unravel one of the fundamental mysteries in neuroscience – how the human brain encodes and makes sense of the flow of time and experiences.
The study, published in the journal Nature, directly recorded the activity of individual neurons in humans and found specific types of brain cells fired in a way that mostly mirrored the order and structure of a person’s experience. They found the brain retains these unique firing patterns after the experience is concluded and can rapidly replay them while at rest.
Furthermore, the brain is also able to utilize these learned patterns to ready itself for future stimuli following that experience. These findings provide the first empirical evidence regarding how specific brain cells integrate “what” and “when” information to extract and retain representations of experiences through time. LINK
Better that than this ...
The US Army Is Testing Killer Robot Dogs With AI-Powered Rifles in the Middle East
It's a dog-eat-dog world for the US Army, which is experimenting with rifle-equipped robot dogs at a Middle Eastern testing facility. As Military.com reports, the branch has deployed at least one new "Lone Wolf" robot-dog to test out its anti-drone capabilities at the Red Sands Integrated Experimentation Center, a joint military research facility in the Saudi kingdom that opened last year.
Manufactured by the newly Korean-owned firm Ghost Robotics, the pioneering maker of gun-toting robot canines, the AI-enhanced machine was described by a branch spokesperson as one of "several" pieces of machinery to be part of its anti-drone arsenal. mil-Quadrupedal-Unmanned-Ground-Vehicle-1800.jpg
It's a dog-eat-dog world for the US Army, which is experimenting with rifle-equipped robot dogs at a Middle Eastern testing facility. As Military.com reports, the branch has deployed at least one new "Lone Wolf" robot-dog to test out its anti-drone capabilities at the Red Sands Integrated Experimentation Center, a joint military research facility in the Saudi kingdom that opened last year.
Manufactured by the newly Korean-owned firm Ghost Robotics, the pioneering maker of gun-toting robot canines, the AI-enhanced machine was described by a branch spokesperson as one of "several" pieces of machinery to be part of its anti-drone arsenal. mil-Quadrupedal-Unmanned-Ground-Vehicle-1800.jpg
New York paralysis patient lifts cup using only his thoughts after receiving AI brain implant
.
LINK
.
LINK
US port strike throws spotlight on big union foe: automation
A strike by dockworkers on the U.S. East Coast and Gulf Coast that disrupted much of the nation's ocean shipping this week ended on Thursday, but a key issue driving labor unrest across the continent - the growing use of automation - was unresolved. Companies view automation as a path to better profit while unions see it as a job-killer. For North American dockworkers battling automation, Europe's port worker contracts may point a way to resolve the issue. LINK
A strike by dockworkers on the U.S. East Coast and Gulf Coast that disrupted much of the nation's ocean shipping this week ended on Thursday, but a key issue driving labor unrest across the continent - the growing use of automation - was unresolved. Companies view automation as a path to better profit while unions see it as a job-killer. For North American dockworkers battling automation, Europe's port worker contracts may point a way to resolve the issue. LINK
Man Gets Prison Sentence for Cloning Giant Sheep
A Montana man has been sentenced to six months in prison — and slapped with over $24,000 in fines — for breeding and selling clones of an enormous, Frankenstein's monster of a sheep. Department of Justice prosecutors say that Arthur "Jack" Schubarth, 81, illegally created the genetic hybrids by using body tissue taken from a specimen of the largest ovine species in the world: the Marco Polo argali sheep. The species can weigh over 300 pounds, stand at some four feet tall, and boast horns longer than five feet.
Through a years-long program of artificial insemination and selective breeding, Schubarth went on to sell his monstrously huge clones to big game hunters, as well as to other breeders.
,
LINK
A Montana man has been sentenced to six months in prison — and slapped with over $24,000 in fines — for breeding and selling clones of an enormous, Frankenstein's monster of a sheep. Department of Justice prosecutors say that Arthur "Jack" Schubarth, 81, illegally created the genetic hybrids by using body tissue taken from a specimen of the largest ovine species in the world: the Marco Polo argali sheep. The species can weigh over 300 pounds, stand at some four feet tall, and boast horns longer than five feet.
Through a years-long program of artificial insemination and selective breeding, Schubarth went on to sell his monstrously huge clones to big game hunters, as well as to other breeders.
,
LINK
A Massive Space Junk Disaster in Orbit Is Inevitable Now, Scientists Warn
Researchers from the orbital mapping firm LeoLabs are raising alarm bells about the dangerous amount of space junk littering our planet's orbit that will inevitably create a catastrophe. ... In an interview with Forbes, LeoLabs senior technical fellow Darren McKnight described the issue as a "ticking time bomb" waiting in the wings.
With our planet veritably surrounded by almost 30,000 objects bigger than a softball hurtling through space at extremely fast speeds, McKnight and his colleagues are looking for solutions to head off tragedy — but they might not be able to make it in time. ... While no human lives have been lost to errant pieces of space debris so far, we've already seen some close calls. Case in point, the damage done to the Canadarm2 robotic arm outside the ISS which had a hole ripped through it by a tiny piece of shrapnel in 2021 ... LINK
Researchers from the orbital mapping firm LeoLabs are raising alarm bells about the dangerous amount of space junk littering our planet's orbit that will inevitably create a catastrophe. ... In an interview with Forbes, LeoLabs senior technical fellow Darren McKnight described the issue as a "ticking time bomb" waiting in the wings.
With our planet veritably surrounded by almost 30,000 objects bigger than a softball hurtling through space at extremely fast speeds, McKnight and his colleagues are looking for solutions to head off tragedy — but they might not be able to make it in time. ... While no human lives have been lost to errant pieces of space debris so far, we've already seen some close calls. Case in point, the damage done to the Canadarm2 robotic arm outside the ISS which had a hole ripped through it by a tiny piece of shrapnel in 2021 ... LINK
scientists discovered living microbes sealed inside a 2-billion-year-old stone.
It's "the oldest example of living microbes being found within ancient rock so far discovered," according to a press release.
"We didn't know if 2-billion-year-old rocks were habitable," said lead study author Yohey Suzuki, an associate professor in the Graduate School of Science at the University of Tokyo, in a statement. "Until now, the oldest geological layer in which living microorganisms had been found was a 100-million-year-old deposit beneath the ocean floor, so this is a very exciting discovery."
In a sense, the rock is something of a time machine. Our current scientific understanding is that the earliest life on Earth emerged about 3.5 billion years ago. Humans, in comparison, have only been around for a few hundred thousand years or so. ... As the researchers write in their study, the microbes, which were confirmed to be indigenous to the stone, appear to have evolved incredibly slowly over time. That means further study into the newly unearthed organisms' genetic makeup could reveal unprecedented insights. ... The ancient stone was discovered in South Africa's Bushvelt Igneous Complex by way of ultradeep drilling. LINK
It's "the oldest example of living microbes being found within ancient rock so far discovered," according to a press release.
"We didn't know if 2-billion-year-old rocks were habitable," said lead study author Yohey Suzuki, an associate professor in the Graduate School of Science at the University of Tokyo, in a statement. "Until now, the oldest geological layer in which living microorganisms had been found was a 100-million-year-old deposit beneath the ocean floor, so this is a very exciting discovery."
In a sense, the rock is something of a time machine. Our current scientific understanding is that the earliest life on Earth emerged about 3.5 billion years ago. Humans, in comparison, have only been around for a few hundred thousand years or so. ... As the researchers write in their study, the microbes, which were confirmed to be indigenous to the stone, appear to have evolved incredibly slowly over time. That means further study into the newly unearthed organisms' genetic makeup could reveal unprecedented insights. ... The ancient stone was discovered in South Africa's Bushvelt Igneous Complex by way of ultradeep drilling. LINK
Rewriting Earth’s History: New Research Reveals That Early Life More Complex Than Imagined
esearchers discovered that Earth’s biodiversity 800 million years ago was richer than previously thought, identifying ancient lineages of organisms that diversified well before the Cambrian explosion. Their findings challenge long-held views about the Neoproterozoic era and highlight the adaptability of early life forms. ... A recent study suggests that by the Neoproterozoic period, distinct lineages of amoebae, as well as the ancestors of plants, algae, and animals, had already emerged and managed to survive the two global glaciations that covered the planet. ... “The classical paradigm for the Neoproterozoic was that there was practically no life on the planet apart from one or two species of bacteria and protists. In the last 15 years, however, fossils of unicellular, eukaryotic, and heterotrophic organisms have been identified at various different locations around the world. These fossils date from about 800 mya [and are termed Tonian]. All this joined our study, which reconstituted the tree of life and used maximum likelihood estimation to identify several well-established Tonian lineages of ancestors of amoebae, animals, fungi, and plants. This radically changes the paradigm for the manner in which the diversification of life occurred on our planet,”
LINK
esearchers discovered that Earth’s biodiversity 800 million years ago was richer than previously thought, identifying ancient lineages of organisms that diversified well before the Cambrian explosion. Their findings challenge long-held views about the Neoproterozoic era and highlight the adaptability of early life forms. ... A recent study suggests that by the Neoproterozoic period, distinct lineages of amoebae, as well as the ancestors of plants, algae, and animals, had already emerged and managed to survive the two global glaciations that covered the planet. ... “The classical paradigm for the Neoproterozoic was that there was practically no life on the planet apart from one or two species of bacteria and protists. In the last 15 years, however, fossils of unicellular, eukaryotic, and heterotrophic organisms have been identified at various different locations around the world. These fossils date from about 800 mya [and are termed Tonian]. All this joined our study, which reconstituted the tree of life and used maximum likelihood estimation to identify several well-established Tonian lineages of ancestors of amoebae, animals, fungi, and plants. This radically changes the paradigm for the manner in which the diversification of life occurred on our planet,”
LINK
Voyager 2 shuts down science experiment as power stores dwindle
The NASA team overseeing the iconic Voyager 2 spacecraft made the decision to power down one of its science instruments in an effort to conserve energy. The probe is currently soaring through space some 13 billion miles (20.9 billion kilometers) from Earth.
Mission engineers sent a command to shutter the Voyager 2’s Plasma Science, or PLS, experiment — which was used to observe solar winds — on September 26 using the Deep Space Network, a series of massive radio antennae that can beam information billions of miles through space.
It took 19 hours for the message to reach Voyager 2, and a return signal was received 19 hours later, NASA said Tuesday.
Despite the aging probe’s emptying power stores, NASA expects that Voyager 2 will keep operating with at least one science instrument into the 2030s. LINK
The NASA team overseeing the iconic Voyager 2 spacecraft made the decision to power down one of its science instruments in an effort to conserve energy. The probe is currently soaring through space some 13 billion miles (20.9 billion kilometers) from Earth.
Mission engineers sent a command to shutter the Voyager 2’s Plasma Science, or PLS, experiment — which was used to observe solar winds — on September 26 using the Deep Space Network, a series of massive radio antennae that can beam information billions of miles through space.
It took 19 hours for the message to reach Voyager 2, and a return signal was received 19 hours later, NASA said Tuesday.
Despite the aging probe’s emptying power stores, NASA expects that Voyager 2 will keep operating with at least one science instrument into the 2030s. LINK
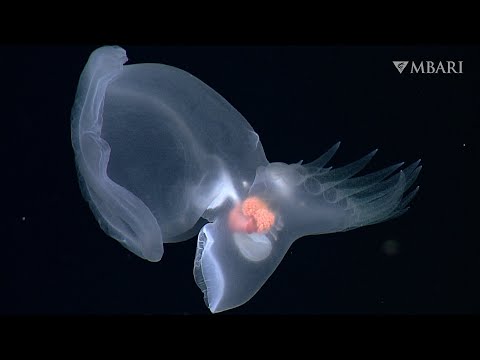
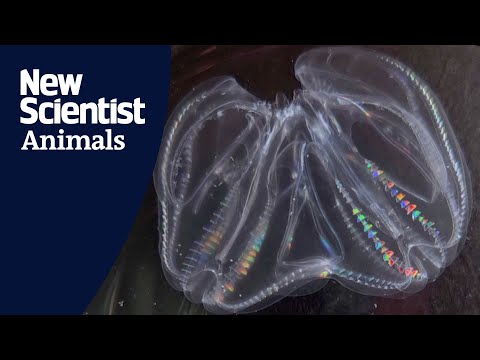
Scientists have discovered, by accident, that warty comb jellyfish can fuse together when injured to form a single organism.
After capturing a bunch of these so-called "sea walnuts" from the western Atlantic Ocean and putting them in saltwater tanks, researchers at the University of Chicago's Marine Biological Lab noticed something odd: one of the creatures seemed much larger than the others, and it had two brains and two butts.
It occurred to the team that they might have a fused-together monstrosity on their hands. To test their theory out, they removed parts of some of the smaller jellies — which, yes, means they intentionally injured them — and put them close together in pairs.
"It turned out that, nine out of ten times, it worked," a statement on the new research reads. "The injured individuals became one, surviving for at least 3 weeks." ... "After a single night, the two original individuals seamlessly became one with no apparent separation between them," the statement explains. "When the researchers poked at one lobe, the whole fused body reacted with a prominent startle response, suggesting that their nervous systems also were fully fused." ... LINK
After capturing a bunch of these so-called "sea walnuts" from the western Atlantic Ocean and putting them in saltwater tanks, researchers at the University of Chicago's Marine Biological Lab noticed something odd: one of the creatures seemed much larger than the others, and it had two brains and two butts.
It occurred to the team that they might have a fused-together monstrosity on their hands. To test their theory out, they removed parts of some of the smaller jellies — which, yes, means they intentionally injured them — and put them close together in pairs.
"It turned out that, nine out of ten times, it worked," a statement on the new research reads. "The injured individuals became one, surviving for at least 3 weeks." ... "After a single night, the two original individuals seamlessly became one with no apparent separation between them," the statement explains. "When the researchers poked at one lobe, the whole fused body reacted with a prominent startle response, suggesting that their nervous systems also were fully fused." ... LINK
stlah





















 Gassho, J stlah
Gassho, J stlah
Comment