No water, no life, no you and me. But where did earth's water come from? A comet clue ...
But our ice ages, also key to you and me, have an outer space connection ...
Now, looking from the stars, to our bodies ...
CRISPR gets crispier! ...
We truly leave traces of ourselves everywhere ...

Gassho, J
stlah
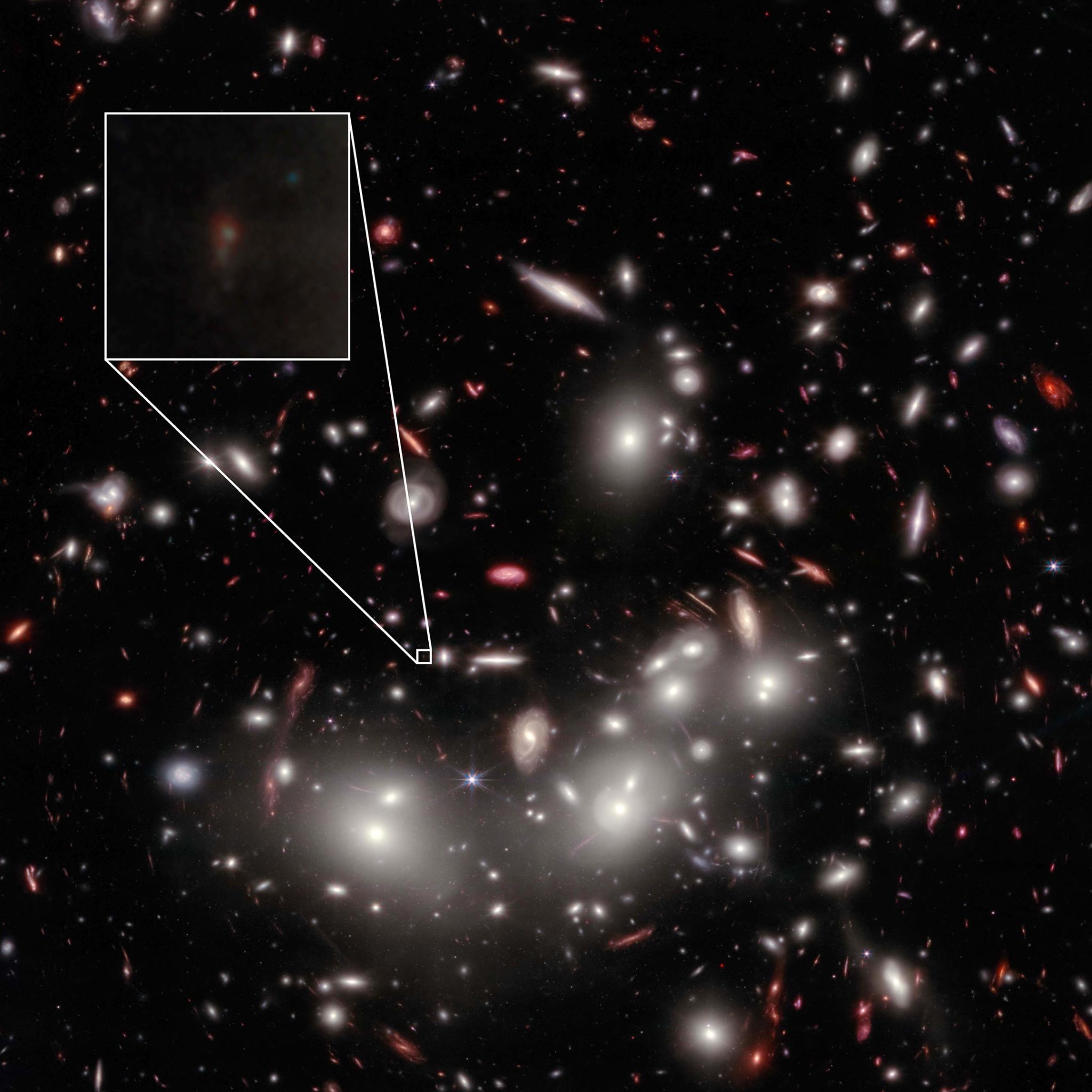
Webb telescope spots water in rare comet
Astronomers used the James Webb Space Telescope to observe a rare comet in our solar system, making a long-awaited scientific breakthrough and stumbling across another mystery at the same time.
For the first time, water was detected in a main belt comet, or a comet located in the main asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The discovery came after 15 years of attempts by astronomers using different observation methods. ... Rather than shedding icy material through sublimation, when a solid turns directly to a gas, the main belt comets only seemed to eject dust. Given their location in the warm inner solar system closer to the sun than typical comets, main belt comets weren’t expected to retain much ice — until now. And the discovery could add more evidence to the theory of how water became a plentiful resource on Earth early in its history.
Comets and water-rich asteroids may have collided with early Earth and delivered water to our planet.
“Our water-soaked world, teeming with life and unique in the universe as far as we know, is something of a mystery — we’re not sure how all this water got here,” said study coauthor Stefanie Milam, Webb deputy project scientist for planetary science at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, in a statement. “Understanding the history of water distribution in the solar system will help us to understand other planetary systems, and if they could be on their way to hosting an Earth-like planet.”
https://us.cnn.com/2023/05/15/world/...scn/index.html
Astronomers used the James Webb Space Telescope to observe a rare comet in our solar system, making a long-awaited scientific breakthrough and stumbling across another mystery at the same time.
For the first time, water was detected in a main belt comet, or a comet located in the main asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The discovery came after 15 years of attempts by astronomers using different observation methods. ... Rather than shedding icy material through sublimation, when a solid turns directly to a gas, the main belt comets only seemed to eject dust. Given their location in the warm inner solar system closer to the sun than typical comets, main belt comets weren’t expected to retain much ice — until now. And the discovery could add more evidence to the theory of how water became a plentiful resource on Earth early in its history.
Comets and water-rich asteroids may have collided with early Earth and delivered water to our planet.
“Our water-soaked world, teeming with life and unique in the universe as far as we know, is something of a mystery — we’re not sure how all this water got here,” said study coauthor Stefanie Milam, Webb deputy project scientist for planetary science at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, in a statement. “Understanding the history of water distribution in the solar system will help us to understand other planetary systems, and if they could be on their way to hosting an Earth-like planet.”
https://us.cnn.com/2023/05/15/world/...scn/index.html
Cosmic Clockwork: The Outer Space Origin of Ice Age Cycle
A team of researchers, including climatologists and an astronomer, has utilized an enhanced computer model to recreate the ice age cycles that occurred between 1.6 and 1.2 million years ago. The findings indicate that the glacial periods were primarily influenced by astronomical forces in quite a different way than it works in the present day. ... The slow, gradual changes in the Earth’s orbit around the Sun and the orientation of its spin axis are influenced by the gravitational forces exerted by the Sun, Moon, and other planets. These astronomical factors impact Earth’s environment by altering the distribution of sunlight and the distinctions between seasons. Ice sheets, in particular, are highly responsive to these external forces, leading to cycles of glacial and interglacial periods. ...
... A team led by Yasuto Watanabe at the University of Tokyo focused on the early Pleistocene Epoch from 1.6 to 1.2 million years ago using an improved climate computer model. Astronomical forces based on modern state-of-the-art theory are considered in these simulations. The large numerical simulations in this study reproduce well the glacial cycle of 40,000 years of the early Pleistocene as indicated by the geological record data.
From the analysis of these simulation results, the team has identified three facts about the mechanisms by which astronomical forces caused changes in climate in those times. (1) The glacial cycle is determined by small differences in the amplitude of variation of the spin axis orientation and the orbit of the Earth. (2) The timing of deglaciation is determined mainly by the position of the summer solstice on its orbit, which is at perihelion, not only by the effect of periodical change of the tilt of the Earth’s axis. (3) The timing of the change in the spin axis orientation and the position of the summer solstice on its orbit determines the duration of the interglacial period.
https://scitechdaily.com/cosmic-cloc...ce-age-cycles/
A team of researchers, including climatologists and an astronomer, has utilized an enhanced computer model to recreate the ice age cycles that occurred between 1.6 and 1.2 million years ago. The findings indicate that the glacial periods were primarily influenced by astronomical forces in quite a different way than it works in the present day. ... The slow, gradual changes in the Earth’s orbit around the Sun and the orientation of its spin axis are influenced by the gravitational forces exerted by the Sun, Moon, and other planets. These astronomical factors impact Earth’s environment by altering the distribution of sunlight and the distinctions between seasons. Ice sheets, in particular, are highly responsive to these external forces, leading to cycles of glacial and interglacial periods. ...
... A team led by Yasuto Watanabe at the University of Tokyo focused on the early Pleistocene Epoch from 1.6 to 1.2 million years ago using an improved climate computer model. Astronomical forces based on modern state-of-the-art theory are considered in these simulations. The large numerical simulations in this study reproduce well the glacial cycle of 40,000 years of the early Pleistocene as indicated by the geological record data.
From the analysis of these simulation results, the team has identified three facts about the mechanisms by which astronomical forces caused changes in climate in those times. (1) The glacial cycle is determined by small differences in the amplitude of variation of the spin axis orientation and the orbit of the Earth. (2) The timing of deglaciation is determined mainly by the position of the summer solstice on its orbit, which is at perihelion, not only by the effect of periodical change of the tilt of the Earth’s axis. (3) The timing of the change in the spin axis orientation and the position of the summer solstice on its orbit determines the duration of the interglacial period.
https://scitechdaily.com/cosmic-cloc...ce-age-cycles/
USC Researchers Zoom Into the Human Genome With Unprecedented Resolution
As part of an international research team, Gazal has made a groundbreaking discovery. They’ve become the first to accurately pinpoint specific base pairs in the human genome that have remained unaltered throughout millions of years of mammalian evolution. These base pairs play a significant role in human disease. Their findings were published in a special Zoonomia edition of the journal Science. Gazal and his team analyzed the genomes of 240 mammals, including humans, zooming in with unprecedented resolution to compare DNA. They were able to identify base pairs that were “constrained” – meaning they remained generally consistent – across mammal species over the course of evolution. Individuals born with mutations on these genes may not have been as successful within their species or were otherwise not likely to pass down the genetic variation. “We were able to identify where gene mutations are not tolerated in evolution, and we demonstrated that these mutations are significant when it comes to disease,” explains Gazal.
The team found that 3.3% of bases in the human genome are “significantly constrained,” including 57.6% of the coding bases that determine amino acid position, meaning these bases had unusually few variants across species in the dataset. The most constrained base pairs in mammals were over seven times more likely to be causal for human disease and complex traits, and over 11 times more likely when researchers looked at the most constrained base pairs in primates alone.
https://scitechdaily.com/usc-researc...ed-resolution/
As part of an international research team, Gazal has made a groundbreaking discovery. They’ve become the first to accurately pinpoint specific base pairs in the human genome that have remained unaltered throughout millions of years of mammalian evolution. These base pairs play a significant role in human disease. Their findings were published in a special Zoonomia edition of the journal Science. Gazal and his team analyzed the genomes of 240 mammals, including humans, zooming in with unprecedented resolution to compare DNA. They were able to identify base pairs that were “constrained” – meaning they remained generally consistent – across mammal species over the course of evolution. Individuals born with mutations on these genes may not have been as successful within their species or were otherwise not likely to pass down the genetic variation. “We were able to identify where gene mutations are not tolerated in evolution, and we demonstrated that these mutations are significant when it comes to disease,” explains Gazal.
The team found that 3.3% of bases in the human genome are “significantly constrained,” including 57.6% of the coding bases that determine amino acid position, meaning these bases had unusually few variants across species in the dataset. The most constrained base pairs in mammals were over seven times more likely to be causal for human disease and complex traits, and over 11 times more likely when researchers looked at the most constrained base pairs in primates alone.
https://scitechdaily.com/usc-researc...ed-resolution/
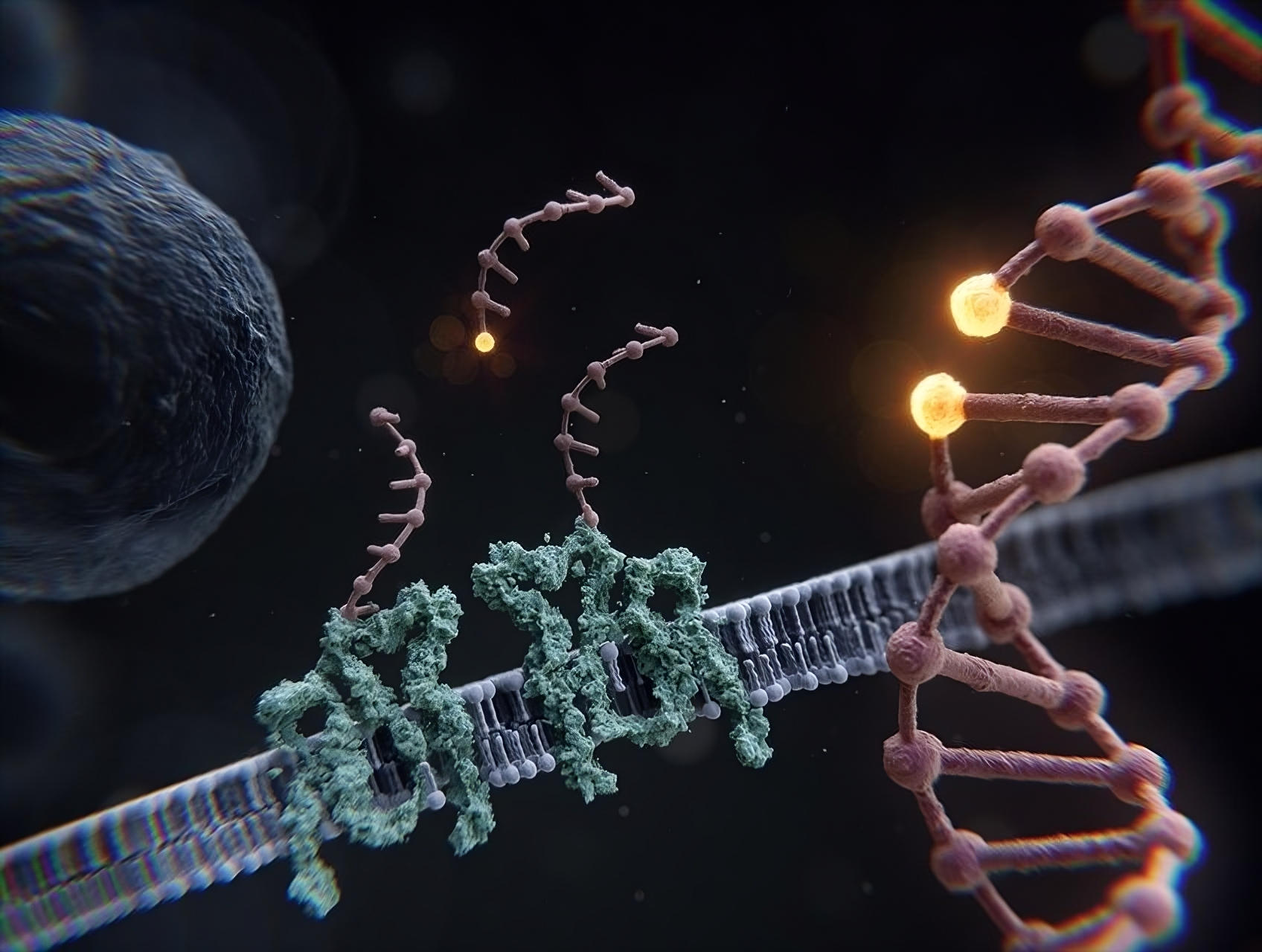
Gene Editing Gets a Triple Boost: “Happy Accident” Leads to Enhanced CRISPR Efficiency
Scientists have enhanced the efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing by threefold using interstrand crosslinks, without resorting to viral material for delivery. This approach boosts the cell’s natural repair mechanisms, allowing for more accurate and efficient gene editing, potentially improving disease research and preclinical work.
https://scitechdaily.com/gene-editin...pr-efficiency/
Scientists have enhanced the efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing by threefold using interstrand crosslinks, without resorting to viral material for delivery. This approach boosts the cell’s natural repair mechanisms, allowing for more accurate and efficient gene editing, potentially improving disease research and preclinical work.
https://scitechdaily.com/gene-editin...pr-efficiency/
Human DNA can now be pulled from thin air or a footprint on the beach. Here’s what that could mean
Footprints left on a beach. Air breathed in a busy room. Ocean water.
Scientists have been able to collect and analyze detailed genetic data from human DNA from all these places, raising thorny ethical questions about consent, privacy and security when it comes to our biological information.
The researchers from the University of Florida, who were using environmental DNA found in sand to study endangered sea turtles, said the DNA was of such high quality that the scientists could identify mutations associated with disease and determine the genetic ancestry of populations living nearby.
... Human DNA that has seeped into the environment through our spit, skin, sweat and blood could be used to help find missing persons, aid in forensic investigations to solve crimes, locate sites of archaeological importance, and for health monitoring through DNA found in waste water, the study noted.
However, the ability to capture human DNA from the environment could have a range of unintended consequences — both inadvertent and malicious, they added. These included privacy breaches, location tracking, data harvesting, and genetic surveillance of individuals or groups. It could lead to ethical hurdles for the approval of wildlife studies.
... Yves Moreau, a professor at the University of Leuven in Belgium who studies artificial intelligence and genetics and has shone a light on China’s DNA sampling of Tibetan and Uyghur minorities, said that while it was possible to imagine a scenario where “a mafia or dictatorship would track a protected witness or a political refugee” using waste water sequencing, it remained “a bit far fetched.”
“We need a political discussion of expectations of privacy in the public space, in particular for DNA. We cannot avoid shedding DNA in the public space,” Moreau, who was not involved in this study, said via email.
https://us.cnn.com/2023/05/15/health...scn/index.html
Footprints left on a beach. Air breathed in a busy room. Ocean water.
Scientists have been able to collect and analyze detailed genetic data from human DNA from all these places, raising thorny ethical questions about consent, privacy and security when it comes to our biological information.
The researchers from the University of Florida, who were using environmental DNA found in sand to study endangered sea turtles, said the DNA was of such high quality that the scientists could identify mutations associated with disease and determine the genetic ancestry of populations living nearby.
... Human DNA that has seeped into the environment through our spit, skin, sweat and blood could be used to help find missing persons, aid in forensic investigations to solve crimes, locate sites of archaeological importance, and for health monitoring through DNA found in waste water, the study noted.
However, the ability to capture human DNA from the environment could have a range of unintended consequences — both inadvertent and malicious, they added. These included privacy breaches, location tracking, data harvesting, and genetic surveillance of individuals or groups. It could lead to ethical hurdles for the approval of wildlife studies.
... Yves Moreau, a professor at the University of Leuven in Belgium who studies artificial intelligence and genetics and has shone a light on China’s DNA sampling of Tibetan and Uyghur minorities, said that while it was possible to imagine a scenario where “a mafia or dictatorship would track a protected witness or a political refugee” using waste water sequencing, it remained “a bit far fetched.”
“We need a political discussion of expectations of privacy in the public space, in particular for DNA. We cannot avoid shedding DNA in the public space,” Moreau, who was not involved in this study, said via email.
https://us.cnn.com/2023/05/15/health...scn/index.html

Gassho, J
stlah


























 ] Japan confirmed the existence of CP violation ... In 2008, Makoto Kobayashi and Toshihide Maskawa received the Nobel Prize in Physics for their theoretical framework that elegantly explained the observed CP violation phenomena.
] Japan confirmed the existence of CP violation ... In 2008, Makoto Kobayashi and Toshihide Maskawa received the Nobel Prize in Physics for their theoretical framework that elegantly explained the observed CP violation phenomena.


Comment