Rev 'er up ...
And some new discoveries ...

The new pentaquark, illustrated here as a pair of standard hadrons loosely bound in a molecule-like structure, is made up of a charm quark and a charm antiquark and an up, a down and a strange quark.
Gassho, J
STLah
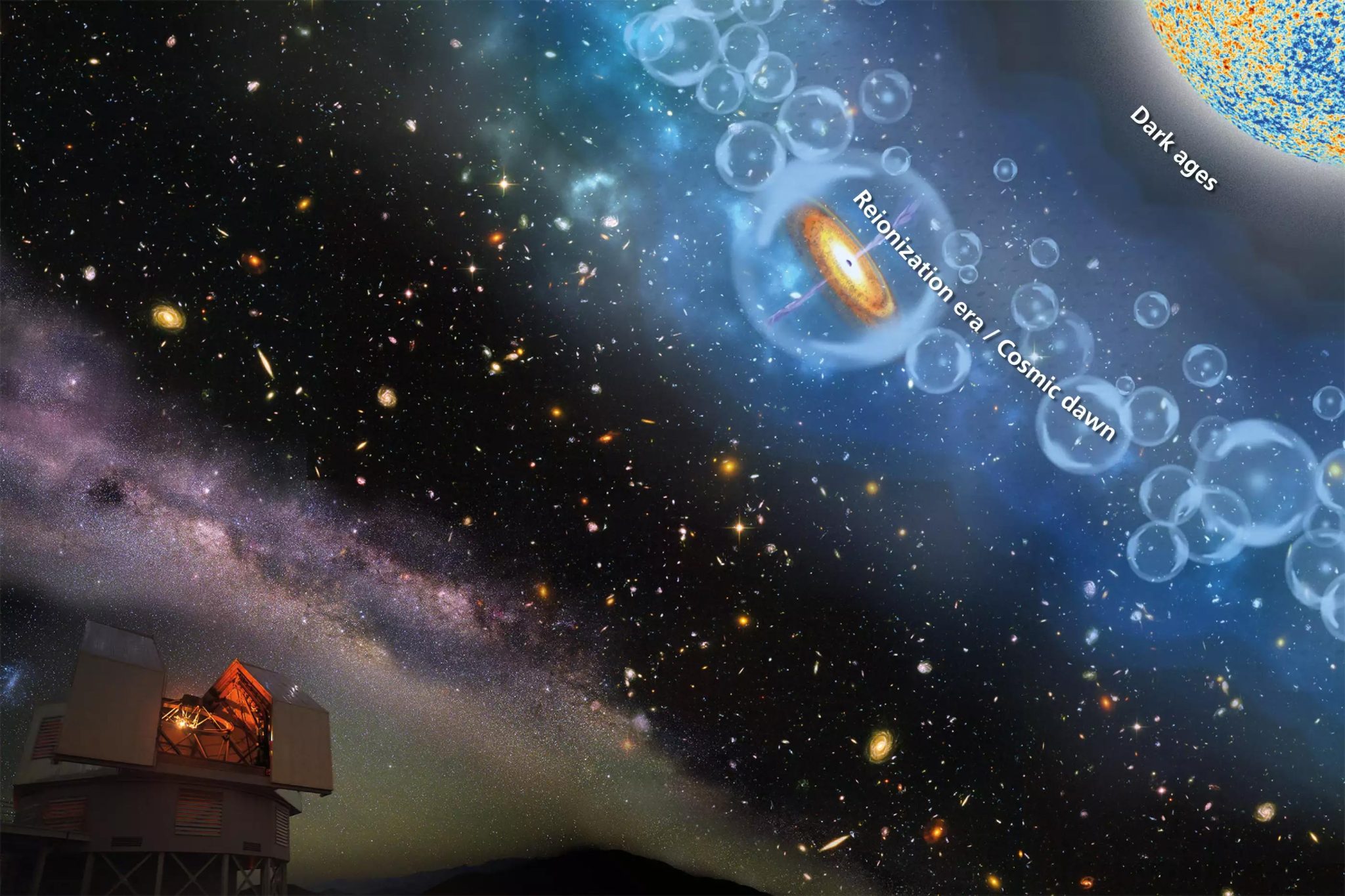
Large Hadron Collider Successfully Restarted at Record Energy: Revving Up the Search for Dark Matter
Following over three years of upgrade and maintenance work, the LHC is now set to run for close to four years at the record energy of 13.6 trillion electronvolts (TeV), providing increased precision and discovery potential. Many factors point to a promising physics season that will further expand the already very diverse LHC physics program: increased collision rates, higher collision energy, upgraded data readout and selection systems, improved detector systems and computing infrastructure.
...
A new period of data taking began on Tuesday, July 5 for the experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the world’s most powerful particle accelerator, after more than three years of upgrade and maintenance work. Beams have already been circulating in CERN’s accelerator complex since April, with the LHC machine and its injectors being recommissioned to operate with new higher-intensity beams and increased energy. However, now the LHC operators have announced “stable beams,” the condition allowing the experiments to switch on all their subsystems and begin taking the data that will be used for physics analysis. The LHC will run around the clock for close to four years at a record energy of 13.6 trillion electronvolts (TeV), providing greater precision and discovery potential than ever before.
https://scitechdaily.com/large-hadro...r-dark-matter/
Following over three years of upgrade and maintenance work, the LHC is now set to run for close to four years at the record energy of 13.6 trillion electronvolts (TeV), providing increased precision and discovery potential. Many factors point to a promising physics season that will further expand the already very diverse LHC physics program: increased collision rates, higher collision energy, upgraded data readout and selection systems, improved detector systems and computing infrastructure.
...
A new period of data taking began on Tuesday, July 5 for the experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the world’s most powerful particle accelerator, after more than three years of upgrade and maintenance work. Beams have already been circulating in CERN’s accelerator complex since April, with the LHC machine and its injectors being recommissioned to operate with new higher-intensity beams and increased energy. However, now the LHC operators have announced “stable beams,” the condition allowing the experiments to switch on all their subsystems and begin taking the data that will be used for physics analysis. The LHC will run around the clock for close to four years at a record energy of 13.6 trillion electronvolts (TeV), providing greater precision and discovery potential than ever before.
https://scitechdaily.com/large-hadro...r-dark-matter/
Three New Exotic Particles Discovered With Large Hadron Collider
Three never-before-seen particles have been observed by the international Large Hadron Collider beauty (LHCb) collaboration at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). The discovery includes a new kind of “pentaquark” and the first-ever pair of “tetraquarks,” which includes a new type of tetraquark.
The findings, presented at a CERN seminar today (July 5, 2022), add three new exotic members to the growing list of new hadrons found at the LHC. They will help physicists better understand how quarks bind together into these composite particles. ... Quarks are elementary particles and can be classified in six flavors: up, down, charm, strange, top, and bottom. They usually combine together in groups of twos and threes to form hadrons such as the protons and neutrons that comprise atomic nuclei. However, on rare occasions, they can also combine into four-quark and five-quark particles, known as “tetraquarks” and “pentaquarks.” These exotic hadrons were predicted by theorists about six decades ago, at the same time as conventional hadrons, but only relatively recently, in the past 20 years, have they been detected by LHCb and other experiments. ... The discoveries announced today by the LHCb collaboration include new kinds of exotic hadrons. The first kind, observed in an analysis of “decays” of negatively charged B mesons, is a pentaquark made up of a charm quark and a charm antiquark and an up, a down and a strange quark. It is the first pentaquark found to contain a strange quark. The finding has a whopping statistical significance of 15 standard deviations, far beyond the 5 standard deviations that are required to claim the observation of a particle in particle physics.
https://scitechdaily.com/three-new-e...dron-collider/
Three never-before-seen particles have been observed by the international Large Hadron Collider beauty (LHCb) collaboration at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). The discovery includes a new kind of “pentaquark” and the first-ever pair of “tetraquarks,” which includes a new type of tetraquark.
The findings, presented at a CERN seminar today (July 5, 2022), add three new exotic members to the growing list of new hadrons found at the LHC. They will help physicists better understand how quarks bind together into these composite particles. ... Quarks are elementary particles and can be classified in six flavors: up, down, charm, strange, top, and bottom. They usually combine together in groups of twos and threes to form hadrons such as the protons and neutrons that comprise atomic nuclei. However, on rare occasions, they can also combine into four-quark and five-quark particles, known as “tetraquarks” and “pentaquarks.” These exotic hadrons were predicted by theorists about six decades ago, at the same time as conventional hadrons, but only relatively recently, in the past 20 years, have they been detected by LHCb and other experiments. ... The discoveries announced today by the LHCb collaboration include new kinds of exotic hadrons. The first kind, observed in an analysis of “decays” of negatively charged B mesons, is a pentaquark made up of a charm quark and a charm antiquark and an up, a down and a strange quark. It is the first pentaquark found to contain a strange quark. The finding has a whopping statistical significance of 15 standard deviations, far beyond the 5 standard deviations that are required to claim the observation of a particle in particle physics.
https://scitechdaily.com/three-new-e...dron-collider/

The new pentaquark, illustrated here as a pair of standard hadrons loosely bound in a molecule-like structure, is made up of a charm quark and a charm antiquark and an up, a down and a strange quark.
Gassho, J
STLah







Comment